Hemin binding protein C is found in outer membrane vesicles and protects Bartonella henselae against toxic concentrations of hemin
- PMID: 22232189
- PMCID: PMC3294634
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05769-11
Hemin binding protein C is found in outer membrane vesicles and protects Bartonella henselae against toxic concentrations of hemin
Abstract
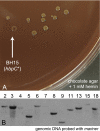
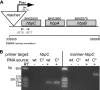
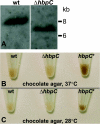
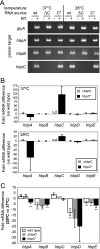
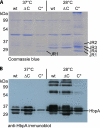
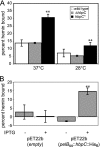
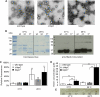
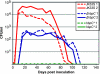
Bartonella species are gram-negative, emerging bacterial pathogens found in two distinct environments. In the gut of the obligately hematophagous arthropod vector, bartonellae are exposed to concentrations of heme that are toxic to other bacteria. In the bloodstream of the mammalian host, access to heme and iron is severely restricted. Bartonellae have unusually high requirements for heme, which is their only utilizable source of iron. Although heme is essential for Bartonella survival, little is known about genes involved in heme acquisition and detoxification. We developed a strategy for high-efficiency transposon mutagenesis to screen for genes in B. henselae heme binding and uptake pathways. We identified a B. henselae transposon mutant that constitutively expresses the hemin binding protein C (hbpC) gene. In the wild-type strain, transcription of B. henselae hbpC was upregulated at arthropod temperature (28°C), compared to mammalian temperature (37°C). In the mutant strain, temperature-dependent regulation was absent. We demonstrated that HbpC binds hemin and localizes to the B. henselae outer membrane and outer membrane vesicles. Overexpression of hbpC in B. henselae increased resistance to heme toxicity, implicating HbpC in protection of B. henselae from the toxic levels of heme present in the gut of the arthropod vector. Experimental inoculation of cats with B. henselae strains demonstrated that both constitutive expression and deletion of hbpC affect the ability of B. henselae to infect the cat host. Modulation of hbpC expression appears to be a strategy employed by B. henselae to survive in the arthropod vector and the mammalian host.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Managing iron supply during the infection cycle of a flea borne pathogen, Bartonella henselae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Oct 18;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00060. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24151576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemin-dependent growth and hemin binding of Bartonella henselae.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 Aug 1;189(1):55-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09205.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10913865
-
Transcriptional regulation of the heme binding protein gene family of Bartonella quintana is accomplished by a novel promoter element and iron response regulator.Infect Immun. 2007 Sep;75(9):4373-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00497-07. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17576755 Free PMC article.
-
Heme binding proteins of Bartonella henselae are required when undergoing oxidative stress during cell and flea invasion.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048408. Epub 2012 Oct 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144761 Free PMC article.
-
Bartonella henselae and the potential for arthropod vector-borne transmission.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011 May;11(5):471-7. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2010.0106. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011. PMID: 20973657 Review.
Cited by
-
A pseudokinase version of the histidine kinase ChrS promotes high heme tolerance of Corynebacterium glutamicum.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 7;13:997448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.997448. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160252 Free PMC article.
-
Prokaryotic microvesicles Ortholog of eukaryotic extracellular vesicles in biomedical fields.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 30;22(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01414-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38291458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bartonella massiliensis sp. nov., a new bacterial species isolated from an Ornithodoros sonrai tick from Senegal.New Microbes New Infect. 2019 Aug 27;32:100596. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2019.100596. eCollection 2019 Nov. New Microbes New Infect. 2019. PMID: 31719993 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles in Human Health and Disease.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 1;13:828704. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.828704. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35300484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing iron supply during the infection cycle of a flea borne pathogen, Bartonella henselae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Oct 18;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00060. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24151576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

