Development and optimization of a novel 384-well anti-malarial imaging assay validated for high-throughput screening
- PMID: 22232455
- PMCID: PMC3247113
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.11-0302
Development and optimization of a novel 384-well anti-malarial imaging assay validated for high-throughput screening
Abstract
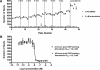
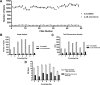
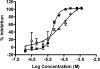
With the increasing occurrence of drug resistance in the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, there is a great need for new and novel anti-malarial drugs. We have developed a 384-well, high-throughput imaging assay for the detection of new anti-malarial compounds, which was initially validated by screening a marine natural product library, and subsequently used to screen more than 3 million data points from a variety of compound sources. Founded on another fluorescence-based P. falciparum growth inhibition assay, the DNA-intercalating dye 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, was used to monitor changes in parasite number. Fluorescent images were acquired on the PerkinElmer Opera High Throughput confocal imaging system and analyzed with a spot detection algorithm using the Acapella data processing software. Further optimization of this assay sought to increase throughput, assay stability, and compatibility with our high-throughput screening equipment platforms. The assay typically yielded Z'-factor values of 0.5-0.6, with signal-to-noise ratios of 12.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An adaptable, fit-for-purpose screening approach with high-throughput capability to determine speed of action and stage specificity of anti-malarial compounds.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Oct 8;68(10):e0074624. doi: 10.1128/aac.00746-24. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39264187 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and continued validation of the malaria SYBR green I-based fluorescence assay for use in malaria drug screening.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun;51(6):1926-33. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01607-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17371812 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying rapidly parasiticidal anti-malarial drugs using a simple and reliable in vitro parasite viability fast assay.Malar J. 2015 Nov 5;14:441. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0962-2. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26542470 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and challenges in the use of fluorescence-based flow cytometric assays for anti-malarial drug susceptibility tests.Malar J. 2021 Jan 21;20(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03591-8. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33478496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools for surveillance of anti-malarial drug resistance: an assessment of the current landscape.Malar J. 2018 Feb 8;17(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2185-9. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 29422048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical signatures and new drug targets for gametocytocidal drug development.Sci Rep. 2014 Jan 17;4:3743. doi: 10.1038/srep03743. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24434750 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of anti-malarial compounds derived from African medicinal plants: a review of pharmacological evaluations from 2013 to 2019.Malar J. 2020 May 18;19(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03231-7. Malar J. 2020. PMID: 32423415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hexahydroquinolines are antimalarial candidates with potent blood-stage and transmission-blocking activity.Nat Microbiol. 2017 Oct;2(10):1403-1414. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0007-4. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Nat Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28808258 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of antiprotozoal drug mechanisms by metabolomics approaches.Parasitology. 2014 Jan;141(1):83-92. doi: 10.1017/S0031182013000814. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Parasitology. 2014. PMID: 23734876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenylated Flavonoids from the Roots of Tephrosia rhodesica.J Nat Prod. 2020 Aug 28;83(8):2390-2398. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00245. Epub 2020 Aug 13. J Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 32790306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . World Malaria Report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Tuteja R. Malaria–an overview. Febs J. 2007;274:4670–4679. - PubMed
-
- Schlitzer M. Malaria chemotherapeutics part I: history of antimalarial drug development, currently used therapeutics, and drugs in clinical development. ChemMedChem. 2007;2:944–986. - PubMed
-
- Gardner MJ, Hall N, Fung E, White O, Berriman M, Hyman RW, Carlton MJ, Pain A, Nelson KE, Rutherford K, Salzberg SL, Craig A, Kyes S, Chan MS, Nene V, Shallom SJ, Suh B, Peterson J, Angiuoli S, Pertea M, Allen J, Selengut J, Haft D, Mather MW, Vaidya AB, Martin DM, Fairlamb AH, Fraunholz MJ, Roos DS, Ralph SA, McFadden GI, Cummings LM, Subramanian GM, Mungall C, Venter JC, Carucci DJ, Hoffman SL, Newbold C, Davis RW, Fraser CM, Barell B. Genome sequence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 2002;419:498–511. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

