Identification of major rice allergen and their clinical significance in children
- PMID: 22232624
- PMCID: PMC3250595
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2011.54.10.414
Identification of major rice allergen and their clinical significance in children
Abstract
Purpose: Recently, an increase in the number of patients sensitized to rice allergen with or without clinical symptoms has been reported. This study was designed to determine the major allergens in rice and their clinical significance.
Methods: Twenty-four children (15 boys and 9 girls; mean age, 16.3 months) with allergic disease, who were sensitized to rice antigen (by UniCAP) in the Pediatric Allergy Respiratory Center at Soonchunhyang University Hospital, were enrolled in this study. The allergenicity of various types of rice (raw, cooked, and heat-treated, simulated gastric fluid [SGF], and simulated intestinal fluid [SIF]) was investigated using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoglobulin E (IgE) immunoblots. The patients' medical records, including laboratory data and allergy symptoms after ingestion of rice were reviewed.
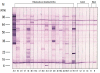
Results: Patients were sensitized to an average of 13.5 food antigens and their mean total IgE was 6,888.7 kU/L. In SDS-PAGE, more than 16 protein bands were observed in the raw rice, whereas only 14-16 kDa and 31-35 kDa protein bands were observed in cooked rice. The common SDS-PAGE protein bands observed in SGF-, SIF-, and heat-treated rice were 9, 14, and 31 kDa. In a heated-rice IgE immunoblot, protein bands of 9, 14, and 31-33 kDa were found in 27.8%, 38.9%, and 38.9% of all sera, respectively, and in 50%, 50%, and 75%, of ser a from the 4 symptomatic patients, respectively.
Conclusion: The 9-, 14-, and 31-kDa protein bands appeared to be the major allergens responsible for rice allergy symptoms.
Keywords: Child; Rice allergen; Sensitization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tropomyosin, the major tropical oyster Crassostrea belcheri allergen and effect of cooking on its allergenicity.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct 26;11:30. doi: 10.1186/s13223-015-0099-4. eCollection 2015. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26504467 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Thermal Treatments on Major and Minor Allergens of Sea Snail, Cerithidea obtusa (Obtuse Horn Shell).Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016 Aug;15(4):309-316. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27921412 Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of tropomyosin and arginine kinase as major allergens of Portunus pelagicus (blue swimming crab).Trop Biomed. 2012 Sep;29(3):467-78. Trop Biomed. 2012. PMID: 23018510
-
Garlic: a potential food allergen?J Food Allergy. 2023 Dec 1;5(2):65-67. doi: 10.2500/jfa.2023.5.230012. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Food Allergy. 2023. PMID: 39022755 Free PMC article.
-
Malaysian cockle (Anadara granosa) allergy: Identification of IgE-binding proteins and effects of different cooking methods.Trop Biomed. 2015 Jun;32(2):323-34. Trop Biomed. 2015. PMID: 26691261
Cited by
-
IgE mediated food allergy in Korean children: focused on plant food allergy.Asia Pac Allergy. 2013 Jan;3(1):15-22. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2013.3.1.15. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Asia Pac Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23403730 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of pea and rice protein fermented by Shiitake (Lentinula edodes) mycelia as a Novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283.EFSA J. 2022 Apr 6;20(4):e07205. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7205. eCollection 2022 Apr. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35414836 Free PMC article.
-
IgE-mediated food allergies in children: prevalence, triggers, and management.Korean J Pediatr. 2017 Apr;60(4):99-105. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.4.99. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Korean J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28461822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ikezawa Z, Miyakawa K, Komatsu H, Suga C, Miyakawa J, Sugiyama A, et al. A probable involvement of rice allergy in severe type of atopic dermatitis in Japan. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1992;176:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Ikezawa Z, Ikebe T, Ogura H, Odajima H, Kurosaka F, Komatu H, et al. Mass trial of hypoallergenic rice (HRS-1) produced by enzymatic digestion in atopic dermatitis with suspected rice allergy. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1992;176:108–112. - PubMed
-
- Nambu M, Shintaku N, Ohta S. Rice allergy. Pediatrics. 2006;117:2331–2332. - PubMed
-
- Lee SY, Jeoung BJ, Kim DS, Kim KE, Lee KY. Detection of specific IgE and IgG4 to rice and its significance in atopic children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1993;3:74–82.
-
- Izumi H, Sugiyama M, Matsuda T, Nakamura R. Structural characterization of the 16-kDa allergen, RA17, in rice seeds. Prediction of the secondary structure and identification of intramolecular disulfide bridges. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999;63:2059–2063. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

