High glucose stimulates glutamate uptakes in pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 22232641
- PMCID: PMC3251763
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.327
High glucose stimulates glutamate uptakes in pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
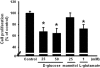
Pancreatic β-cells are major cells responsible for glucose metabolism in the body. Hyperglycemia is known to be a primary factor in the induction of diabetes mellitus. Glutamate is also an excitatory neurotransmitter in diverse organs. Oxidative stress also plays a pivotal role in the development of diabetes mellitus. However, the effect of hyperglycemia in glutamate uptake in the pancreas is not clear. Furthermore, the relationship between high glucose-induced glutamate uptake and oxidative stress has not been investigated. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the effect of high glucose on glutamate uptake in pancreatic β-cells. In the present study, 25 mM glucose stimulated the glutamate uptake in HIT-15 cells of hamster pancreatic β-cells. The treatment of 25 mM glucose and 1 mM glutamate also decreased the cell viability in HIT-15 cells. In addition, the treatment of 25 mM glucose induced an increase of lipid peroxide formation. High glucose-induced increase of LPO formation was prevented by the treatment of antioxidants such as N-acetyl-L-cysteine and quercetin. Furthermore, high glucose-induced stimulation of glutamate uptake and decrease of cell viability were also blocked by the treatment of N-acetyl-L-cysteine and quercetin. In conclusion, high glucose stimulated glutamate uptake via oxidative stress in pancreatic β-cells.
Keywords: Pancreatic β-cells; glutamate uptake; hyperglycemia; oxidative stress.
Figures


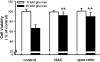
Similar articles
-
Quercetin potentiates insulin secretion and protects INS-1 pancreatic β-cells against oxidative damage via the ERK1/2 pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;161(4):799-814. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00910.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20860660 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin attenuates 2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced oxidative cell damage in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(1):121-6. doi: 10.1248/bpb.35.121. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 22223348
-
System χc- overexpression prevents 2-deoxy-d-ribose-induced β-cell damage.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Jun;153:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.04.012. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32305647
-
CDATA[The Effect of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Therapies on Pancreatic β-cell Dysfunction: Results from in Vitro and in Vivo Studies.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(7):1328-1346. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200526135642. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32452321 Review.
-
Glucose toxicity in beta-cells: type 2 diabetes, good radicals gone bad, and the glutathione connection.Diabetes. 2003 Mar;52(3):581-7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.3.581. Diabetes. 2003. PMID: 12606496 Review.
References
-
- Martens GA, Pipeleers D. Glucose, regulator of survival and phenotype of pancreatic beta cells. Vitam Horm. 2009;80:507–539. - PubMed
-
- Thorens B. Glucose sensing and the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32:S62–S71. - PubMed
-
- Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, van Haeften TW. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Res. 2007;32(1-2):19–37. - PubMed
-
- Spooren W, Lesage A, Lavreysen H, Gasparini F, Steckler T. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: their therapeutic potential in anxiety. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010;2:391–413. - PubMed
-
- Yasuo T, Kusuhara Y, Yasumatsu K, Ninomiya Y. Multiple receptor systems for glutamate detection in the taste organ. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31(10):1833–1837. - PubMed

