Digital RNA sequencing minimizes sequence-dependent bias and amplification noise with optimized single-molecule barcodes
- PMID: 22232676
- PMCID: PMC3268301
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1118018109
Digital RNA sequencing minimizes sequence-dependent bias and amplification noise with optimized single-molecule barcodes
Abstract
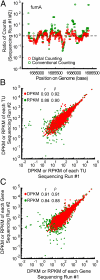
RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) is a powerful tool for transcriptome profiling, but is hampered by sequence-dependent bias and inaccuracy at low copy numbers intrinsic to exponential PCR amplification. We developed a simple strategy for mitigating these complications, allowing truly digital RNA-Seq. Following reverse transcription, a large set of barcode sequences is added in excess, and nearly every cDNA molecule is uniquely labeled by random attachment of barcode sequences to both ends. After PCR, we applied paired-end deep sequencing to read the two barcodes and cDNA sequences. Rather than counting the number of reads, RNA abundance is measured based on the number of unique barcode sequences observed for a given cDNA sequence. We optimized the barcodes to be unambiguously identifiable, even in the presence of multiple sequencing errors. This method allows counting with single-copy resolution despite sequence-dependent bias and PCR-amplification noise, and is analogous to digital PCR but amendable to quantifying a whole transcriptome. We demonstrated transcriptome profiling of Escherichia coli with more accurate and reproducible quantification than conventional RNA-Seq.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Harvard University has filed a provisional patent application based on this work.
Figures
References
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5:621–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

