Digoxin inhibits development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in mice
- PMID: 22232678
- PMCID: PMC3268303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1120385109
Digoxin inhibits development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in mice
Abstract
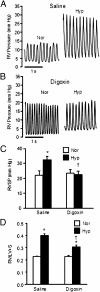
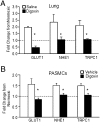
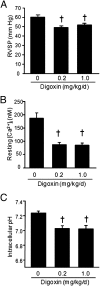
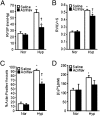
Chronic hypoxia is an inciting factor for the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. The mechanisms involved in the development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH) include hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)-dependent transactivation of genes controlling pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell (PASMC) intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) and pH. Recently, digoxin was shown to inhibit HIF-1 transcriptional activity. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that digoxin could prevent and reverse the development of HPH. Mice were injected daily with saline or digoxin and exposed to room air or ambient hypoxia for 3 wk. Treatment with digoxin attenuated the development of right ventricle (RV) hypertrophy and prevented the pulmonary vascular remodeling and increases in PASMC [Ca(2+)](i), pH, and RV pressure that occur in mice exposed to chronic hypoxia. When started after pulmonary hypertension was established, digoxin attenuated the hypoxia-induced increases in RV pressure and PASMC pH and [Ca(2+)](i). These preclinical data support a role for HIF-1 inhibitors in the treatment of HPH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tuder RM, Yun JH, Bhunia A, Fijalkowska I. Hypoxia and chronic lung disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85:1317–1324. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(12, Suppl S):13S–24S. - PubMed
-
- Rios EJ, Fallon M, Wang J, Shimoda LA. Chronic hypoxia elevates intracellular pH and activates Na+/H+ exchange in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;289:L867–L874. - PubMed
-
- Shimoda LA, Fallon M, Pisarcik S, Wang J, Semenza GL. HIF-1 regulates hypoxic induction of NHE1 expression and alkalinization of intracellular pH in pulmonary arterial myocytes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;291:L941–L949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

