In vitro sensitization of T cells with DC-associated/delivered HIV constructs can induce a polyfunctional CTL response, memory T-cell response, and virus suppression
- PMID: 22233251
- PMCID: PMC3271377
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2011.0055
In vitro sensitization of T cells with DC-associated/delivered HIV constructs can induce a polyfunctional CTL response, memory T-cell response, and virus suppression
Abstract
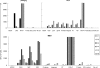
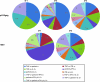
The absence of a suitable animal model for HIV infection is one of the major obstacles to the development of a preventive HIV vaccine. Vaccines showing good response in animal studies may fail in human efficacy trials. We have demonstrated DC-mediated in vitro sensitization of autologous T cells against three HIV constructs. The in vitro sensitized T cells were able to demonstrate a polyfunctional T-cell response, as well as central and effector memory T cells, and virus lysis in a virus inhibition assay, three potentially protective responses. However, none of the constructs could induce all three responses. Also there were variations from volunteer to volunteer. These may be due to genetic and other factors. This study provides evidence of an in vitro system that can be used to assess the immune response against a candidate vaccine, and may also provide the opportunity to modify vaccine constructs to achieve the goal of developing an ideal vaccine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The HIV/AIDS vaccine candidate MVA-B administered as a single immunogen in humans triggers robust, polyfunctional, and selective effector memory T cell responses to HIV-1 antigens.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11468-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05165-11. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21865377 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effective Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Targeting of Persistent HIV-1 during Antiretroviral Therapy Requires Priming of Naive CD8+ T Cells.mBio. 2016 May 31;7(3):e00473-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00473-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27247230 Free PMC article.
-
HIV type 1 vaccine-induced T cell memory and cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in HIV type 1-uninfected volunteers.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001 Aug 10;17(12):1175-89. doi: 10.1089/088922201316912781. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001. PMID: 11522187 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection.APMIS. 2003 Jul-Aug;111(7-8):776-88. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0463.2003.11107809.x. APMIS. 2003. PMID: 12974779 Review.
-
T lymphocyte responses in HIV-1 infection: implications for vaccine development.Curr Opin Immunol. 1999 Aug;11(4):451-9. doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(99)80076-4. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10448136 Review.
Cited by
-
Human dendritic cell targeting peptide can be targeted to porcine dendritic cells to improve antigen capture efficiency to stimulate stronger immune response.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 19;13:950597. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.950597. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059519 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Vaccination With Dendritic Cells Loaded With Autologous HIV Type 1-Infected Apoptotic Cells.J Infect Dis. 2016 May 1;213(9):1400-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv582. Epub 2015 Dec 8. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26647281 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Billaud J. Yagello M. Gluckman JC. Primary in vitro sensitization of human T-helper lymphocytes by peptides derived from the V3 loop of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein. Vaccine. 1994;12:46–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

