A role for the sensory neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide in endothelial cell proliferation in vivo
- PMID: 22233274
- PMCID: PMC3417445
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01848.x
A role for the sensory neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide in endothelial cell proliferation in vivo
Abstract
Background and purpose: We have tested the hypothesis that calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a mediator of capsaicin-induced angiogenesis in vivo.
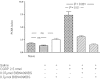
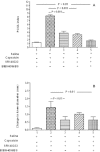
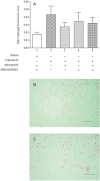
Experimental approach: In a series of experiments, the knee joints of rats were injected with CGRP, capsaicin or vehicle control. Groups of animals (n=6) were treated with the CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS and/or the NK₁ receptor antagonist SR140333. Endothelium, proliferating endothelial cell nuclei and macrophages were identified 24 h later in the synovium by immunohistochemistry and quantified by image analysis. mRNA for the receptors for CGRP and adrenomedullin were sought in normal and inflamed rat and human synovia using RT-PCR.
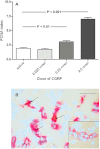
Key results: Intra-articular CGRP injection increased the endothelial cell proliferation index, whereas macrophage infiltration and knee joint diameters were similar to saline-injected controls. CGRP-induced endothelial cell proliferation was dose-dependently inhibited by BIBN4096BS. mRNA for adrenomedullin and the CGRP receptor subunits were detected in normal and inflamed human and rat synovia. In capsaicin-induced synovitis, the increased endothelial cell proliferation index was partially blocked by administration of NK₁ or CGRP antagonists individually and was reduced to the level of saline controls by coadministration of both receptor antagonists.
Conclusions and implications: These data support the hypothesis that CGRP stimulates angiogenesis in vivo directly by activating CGRP receptors. Capsaicin-induced endothelial cell proliferation was completely blocked by coadministration of CGRP and NK₁ receptor antagonists, indicating that both CGRP and substance P may contribute to angiogenesis in this model of synovitis.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Binding and functional pharmacological characteristics of gepant-type antagonists in rat brain and mesenteric arteries.Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;90:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28192258
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits chemokine production by human dermal microvascular endothelial cells.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 May;25(4):787-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.007. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21334428 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of BIBN4096BS, CGRP(8-37), a CGRP antibody and an RNA-Spiegelmer on CGRP induced vasodilatation in the perfused and non-perfused rat middle cerebral artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;150(5):633-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707134. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17245362 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin and calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors in endocrine-related cancers: opportunities and challenges.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010 Dec 13;18(1):C1-14. doi: 10.1677/ERC-10-0244. Print 2011 Feb. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21051558 Review.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the joint: contributions to pain and inflammation.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;80(5):965-78. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12669. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25923821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012 May 29;8(7):390-8. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.80. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22641138 Review.
-
Novel roles of perivascular nerves on neovascularization.Neurol Sci. 2015 Mar;36(3):353-60. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-2016-x. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25432439 Review.
-
Peripheral neuronal sensitization and neurovascular remodelling in osteoarthritis pain.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01280-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40796685 Review.
-
No pain, no gain? The effects of pain-promoting neuropeptides and neurotrophins on fracture healing.Bone. 2020 Feb;131:115109. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.115109. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Bone. 2020. PMID: 31715336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Procedural Overview of the Involvement of Small Molecules in the Nervous System in the Regulation of Bone Healing.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jan 31;20:1263-1284. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S505677. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39906525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman R, Alarcon G, Appelrouth D, Bloch D, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf S, Mapp PI, Walsh DA. Angiogenesis and the persistence of inflammation in a rat model of proliferative synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1890–1898. - PubMed
-
- Buckley TL, Brain SD, Collins PD, Williams TJ. Inflammatory edema induced by interactions between IL-1 and the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide. J Immunol. 1991;146:3424–3430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

