Positron emission tomography assessment of 8-OH-DPAT-mediated changes in an index of cerebral glucose metabolism in female marmosets
- PMID: 22233732
- PMCID: PMC3763841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.065
Positron emission tomography assessment of 8-OH-DPAT-mediated changes in an index of cerebral glucose metabolism in female marmosets
Abstract
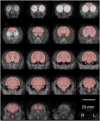
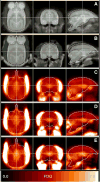
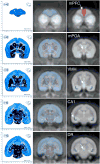
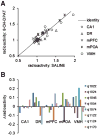
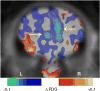
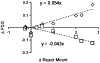
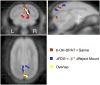
As part of a larger experiment investigating serotonergic regulation of female marmoset sexual behavior, this study was designed to (1) advance methods for PET imaging of common marmoset monkey brain, (2) measure normalized FDG uptake as an index of local cerebral metabolic rates for glucose, and (3) study changes induced in this index of cerebral glucose metabolism by chronic treatment of female marmosets with a serotonin 1A receptor (5-HT(1A)) agonist. We hypothesized that chronic treatment with the 5-HT(1A) agonist 8-OH-DPAT would alter the glucose metabolism index in dorsal raphe (DR), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), medial preoptic area of hypothalamus (mPOA), ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus (VMH), and field CA1 of hippocampus. Eight adult ovariectomized female common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) were studied with and without estradiol replacement. In a crossover design, each subject was treated daily with 8-OH-DPAT (0.1mg/kg SC daily) or saline. After 42-49 days of treatment, the glucose metabolism radiotracer FDG was administered to each female immediately prior to 30 min of interaction with her male pairmate, after which the subject was anesthetized and imaged by PET. Whole brain normalized PET images were analyzed with anatomically defined regions of interest (ROI). Whole brain voxelwise mapping was also used to explore treatment effects and correlations between alterations in the glucose metabolism index and pairmate interactions. The rank order of normalized FDG uptake was VMH/mPOA>DR>mPFC/CA1 in both conditions. 8-OH-DPAT did not induce alterations in the glucose metabolism index in ROIs. Voxelwise mapping showed a significant reduction in normalized FDG uptake in response to 8-OH-DPAT in a cluster in medial occipital cortex as well as a significant correlation between increased rejection of mount attempts and reduced normalized FDG uptake in an overlapping cluster. In conclusion, PET imaging has been used to measure FDG uptake relative to whole brain in marmoset monkeys. Voxelwise mapping shows that 8-OH-DPAT reduces this index of glucose metabolism in medial occipital cortex, consistent with alterations in female sexual behavior.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flibanserin-Stimulated Partner Grooming Reflects Brain Metabolism Changes in Female Marmosets.J Sex Med. 2015 Dec;12(12):2256-66. doi: 10.1111/jsm.13068. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Sex Med. 2015. PMID: 26635207 Free PMC article.
-
Brain region-specific transcriptomic markers of serotonin-1A receptor agonist action mediating sexual rejection and aggression in female marmoset monkeys.J Sex Med. 2013 Jun;10(6):1461-75. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12131. Epub 2013 Apr 2. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 23551660
-
Chronic systemic administration of serotonergic ligands flibanserin and 8-OH-DPAT enhance HPA axis responses to restraint in female marmosets.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Jan;38(1):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 22727480
-
Flibanserin and 8-OH-DPAT implicate serotonin in association between female marmoset monkey sexual behavior and changes in pair-bond quality.J Sex Med. 2012 Mar;9(3):694-707. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02616.x. Epub 2012 Feb 3. J Sex Med. 2012. PMID: 22304661 Free PMC article.
-
8-OH-DPAT influences extracellular levels of serotonin and dopamine in the medial preoptic area of male rats.Brain Res. 1998 Apr 20;790(1-2):217-23. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00065-1. Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9593901
Cited by
-
The marmoset monkey: a multi-purpose preclinical and translational model of human biology and disease.Drug Discov Today. 2012 Nov;17(21-22):1160-5. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Drug Discov Today. 2012. PMID: 22728226 Free PMC article.
-
Flibanserin-Stimulated Partner Grooming Reflects Brain Metabolism Changes in Female Marmosets.J Sex Med. 2015 Dec;12(12):2256-66. doi: 10.1111/jsm.13068. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Sex Med. 2015. PMID: 26635207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott DH, Barnett DK, Colman RJ, Yamamoto ME, Schultz-Darken NJ. Aspects of common marmoset basic biology and life history important for biomedical research. Comp Med. 2003;53(4):339–350. - PubMed
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Afonso VM, Sison M, Lovic V, Fleming AS. Medial prefrontal cortex lesions in the female rat affect sexual and maternal behavior and their sequential organization. Behav Neurosci. 2007;121(3):515–526. - PubMed
-
- Ahlenius S, Fernandezguasti A, Hjorth S, Larsson K. Suppression of lordosis behavior by the putative 5-ht receptor agonist 8-oh-dpat in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986;124(3):361–363. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG. The primate amygdala and the neurobiology of social behavior: implications for understanding social anxiety. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;51(1):11–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

