A mutation in the interferon regulatory element of HBV may influence the response of interferon treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 22233973
- PMCID: PMC3287143
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-10
A mutation in the interferon regulatory element of HBV may influence the response of interferon treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients
Abstract
Background: A functional interferon regulatory element (IRE) has been found in the EnhI/X promoter region of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome. The purpose of this study is to compare the gene order of responder and non-responder to interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), so as to evaluate the relationship between IRE mutation and the response to interferon treatment for CHB patients.
Results: Synthetic therapeutic effect is divided into complete response (CR), partial response (PR) and non-response (NR). Among the 62 cases included in this study, 40 cases (64.5%) were in the response group (CR and PR) and 22 (35.5%) cases were in the NR group. Wild type sequence of HBV IRE TTTCACTTTC were found in 35 cases (56.5%), and five different IRE gene sequences. included TTTtACTTTC, TTTCAtTTTC, TTTtAtTTTC, TTTtACTTTt and cTTtACcTTC, were found in 22 cases (35.5%), 1 case (1.6%), 1 case (1.6%), 2 cases (3.2%) and 1 case (1.6%) respectively. There were 41.9%cases (26/62) with forth base C→T mutation, consisted of 32.5% (13/40) cases in response group and 59.1% (13/22) cases in NR group. Among the 35 cases with IRE sequences, there were 67.5% (27/40) cases in response group and 36.4% (8/22) in NR group, and the difference in IRE sequences between two groups was statistic significantly (P = 0.027). The result suggested that there is likely relationship between the forth base mutation (C→T) of IRE region and the response of HBV to Interferon therapy, and this mutation may partially decrease the inhibition effect of interferon on HBV.
Conclusion: The forth base C→T mutation in IRE element of HBV may partially influence the response of Interferon treatment in CHB patients.
Figures
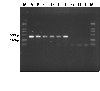
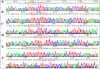
Similar articles
-
[Relationship between Shenzhen HBV genotype and precore/core promoter mutation and antiviral effects].Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Mar;20(1):30-2. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16642214 Chinese.
-
HBV core region variability: effect of antiviral treatments on main epitopic regions.Antivir Ther. 2011;16(1):37-49. doi: 10.3851/IMP1701. Antivir Ther. 2011. PMID: 21311107
-
Association of characteristics of HBV quasispecies with hepatitis B surface antigen seroconversion after pegylated interferon-α-2a treatment in child patients.Antivir Ther. 2018;23(7):567-574. doi: 10.3851/IMP3262. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Antivir Ther. 2018. PMID: 30095435
-
Next generation sequencing identifies baseline viral mutants associated with treatment response to pegylated interferon in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.Virus Genes. 2019 Oct;55(5):610-618. doi: 10.1007/s11262-019-01689-5. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Virus Genes. 2019. PMID: 31359359
-
[Efficacy and problems in combination therapy using lamivudine and interferon for chronic hepatitis B].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Aug;62 Suppl 8:326-30. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15453339 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The response of hepatitis B virus genotype to interferon is associated with a mutation in the interferon-stimulated response element.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(51):e18442. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018442. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31861015 Free PMC article.
-
Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Associated Genotypes among HBsAg-negative Subjects in Burkina Faso.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 1;10(1):e2018007. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.007. eCollection 2018. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29326804 Free PMC article.
-
HBV preS Mutations Promote Hepatocarcinogenesis by Inducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Upregulating Inflammatory Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;14(13):3274. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133274. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35805045 Free PMC article.
-
Peg-Interferon Lambda Treatment Induces Robust Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients.Front Immunol. 2017 May 29;8:621. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00621. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28611778 Free PMC article.
-
Control of hepatitis B virus replication by interferons and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 7;20(33):11618-29. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11618. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25206268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, Iloeje U, Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus. Journal of clinical gastroenterology. 2004;38:S158–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

