Androgens and adipose tissue in males: a complex and reciprocal interplay
- PMID: 22235202
- PMCID: PMC3253446
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/789653
Androgens and adipose tissue in males: a complex and reciprocal interplay
Abstract
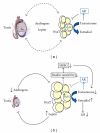
Clinical evidence shows that in males obesity is frequently associated with hypogonadism and vice versa; also, low testosterone levels have been considered a "hallmark" of metabolic syndrome in men. These observations indicate that there is a strict connection between anatomically and functionally distinct cell types such as white adipocytes and Leydig cells, that synthesize testosterone. Adipose tissue is able to control several functions of the testis through its products secreted in the bloodstream. On the other hand, circulating levels of testosterone and estradiol deeply affect adipocyte proliferation, differentiation, and fat mass distribution, hereby controlling critical metabolic functions, such as food intake, insulin sensitivity, vascular reactivity, and immunity. This paper highlights the existing clinical and experimental evidence linking androgens and adipose tissue and illustrates the consequences occurring when the balance between fat mass distribution and eugonadism is lost.
Figures
References
-
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2004;89(6):2548–2556. - PubMed
-
- Armani A, Mammi C, Marzolla V, et al. Cellular models for understanding adipogenesis, adipose dysfunction, and obesity. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 2010;110(3):564–572. - PubMed
-
- Caprio M, Fabbrini E, Isidori AM, Aversa A, Fabbri A. Leptin in reproduction. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2001;12(2):65–72. - PubMed
-
- Carmen GY, Víctor SM. Signalling mechanisms regulating lipolysis. Cellular Signalling. 2006;18(4):401–408. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

