Interferon and biologic signatures in dermatomyositis skin: specificity and heterogeneity across diseases
- PMID: 22235269
- PMCID: PMC3250414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029161
Interferon and biologic signatures in dermatomyositis skin: specificity and heterogeneity across diseases
Abstract
Background: Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune disease that mainly affects the skin, muscle, and lung. The pathogenesis of skin inflammation in DM is not well understood.
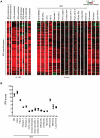
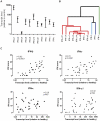
Methodology and findings: We analyzed genome-wide expression data in DM skin and compared them to those from healthy controls. We observed a robust upregulation of interferon (IFN)-inducible genes in DM skin, as well as several other gene modules pertaining to inflammation, complement activation, and epidermal activation and differentiation. The interferon (IFN)-inducible genes within the DM signature were present not only in DM and lupus, but also cutaneous herpes simplex-2 infection and to a lesser degree, psoriasis. This IFN signature was absent or weakly present in atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, acne vulgaris, systemic sclerosis, and localized scleroderma/morphea. We observed that the IFN signature in DM skin appears to be more closely related to type I than type II IFN based on in vitro IFN stimulation expression signatures. However, quantitation of IFN mRNAs in DM skin shows that the majority of known type I IFNs, as well as IFN g, are overexpressed in DM skin. In addition, both IFN-beta and IFN-gamma (but not other type I IFN) transcript levels were highly correlated with the degree of the in vivo IFN transcriptional response in DM skin.
Conclusions and significance: As in the blood and muscle, DM skin is characterized by an overwhelming presence of an IFN signature, although it is difficult to conclusively define this response as type I or type II. Understanding the significance of the IFN signature in this wide array of inflammatory diseases will be furthered by identification of the nature of the cells that both produce and respond to IFN, as well as which IFN subtype is biologically active in each diseased tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Mammen AL. Dermatomyositis and polymyositis: Clinical presentation, autoantibodies, and pathogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1184:134–153. - PubMed
-
- O'Hanlon TP, Miller FW. Genetic risk and protective factors for the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg SA, Amato AA. Uncertainties in the pathogenesis of adult dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2004;17:359–364. - PubMed
-
- Arahata K, Engel AG. Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. I: Quantitation of subsets according to diagnosis and sites of accumulation and demonstration and counts of muscle fibers invaded by T cells. Ann Neurol. 1984;16:193–208. - PubMed
-
- Page G, Chevrel G, Miossec P. Anatomic localization of immature and mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: Interaction with chemokines and Th1 cytokine-producing cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:199–208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

