Receptor heteromerization expands the repertoire of cannabinoid signaling in rodent neurons
- PMID: 22235275
- PMCID: PMC3250422
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029239
Receptor heteromerization expands the repertoire of cannabinoid signaling in rodent neurons
Abstract
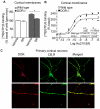
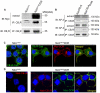
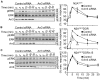
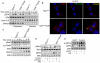
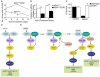
A fundamental question in G protein coupled receptor biology is how a single ligand acting at a specific receptor is able to induce a range of signaling that results in a variety of physiological responses. We focused on Type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB₁R) as a model GPCR involved in a variety of processes spanning from analgesia and euphoria to neuronal development, survival and differentiation. We examined receptor dimerization as a possible mechanism underlying expanded signaling responses by a single ligand and focused on interactions between CB₁R and delta opioid receptor (DOR). Using co-immunoprecipitation assays as well as analysis of changes in receptor subcellular localization upon co-expression, we show that CB₁R and DOR form receptor heteromers. We find that heteromerization affects receptor signaling since the potency of the CB₁R ligand to stimulate G-protein activity is increased in the absence of DOR, suggesting that the decrease in CB₁R activity in the presence of DOR could, at least in part, be due to heteromerization. We also find that the decrease in activity is associated with enhanced PLC-dependent recruitment of arrestin3 to the CB₁R-DOR complex, suggesting that interaction with DOR enhances arrestin-mediated CB₁R desensitization. Additionally, presence of DOR facilitates signaling via a new CB₁R-mediated anti-apoptotic pathway leading to enhanced neuronal survival. Taken together, these results support a role for CB₁R-DOR heteromerization in diversification of endocannabinoid signaling and highlight the importance of heteromer-directed signal trafficking in enhancing the repertoire of GPCR signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
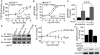
Similar articles
-
The cannabinoid receptor CB1 modulates the signaling properties of the lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 28;287(53):44234-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.364109. Epub 2012 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23161546 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization with cannabinoid receptors allosterically modulates delta opioid receptor activity during neuropathic pain.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e49789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049789. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272051 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological data of cannabidiol- and cannabigerol-type phytocannabinoids acting on cannabinoid CB1, CB2 and CB1/CB2 heteromer receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104940. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104940. Epub 2020 May 26. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32470563
-
Arrestin recruitment and signaling by G protein-coupled receptor heteromers.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jul 1;152:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30419245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and consequences of delta-opioid receptor internalization.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2005;17(1):1-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v17.i1.10. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16307525 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Cannabinoid Signaling in the Immune System: "High"-ly Exciting Questions, Possibilities, and Challenges.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 10;8:1487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01487. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29176975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delta opioid receptors engage multiple signaling cascades to differentially modulate prefrontal GABA release with input and target specificity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:2024.08.08.607246. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.08.607246. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Feb 25;44(2):115293. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115293. PMID: 39149233 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Targeting Cannabinoid 1 and Delta Opioid Receptor Heteromers Alleviates Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019 Aug 9;2(4):219-229. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00008. Epub 2019 Jun 5. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31565698 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo opioid receptor heteromerization: where do we stand?Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):420-34. doi: 10.1111/bph.12702. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24666391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cannabinoid receptor CB1 modulates the signaling properties of the lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 28;287(53):44234-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.364109. Epub 2012 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23161546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berghuis P, Rajnicek AM, Morozov YM, Ross RA, Mulder J, et al. Hardwiring the brain: endocannabinoids shape neuronal connectivity. Science. 2007;316:1212–1216. - PubMed
-
- Harkany T, Keimpema E, Barabas K, Mulder J. Endocannabinoid functions controlling neuronal specification during brain development. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;286:S84–90. - PubMed
-
- Guzman M, Sanchez C, Galve-Roperh I. Cannabinoids and cell fate. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;95:175–184. - PubMed
-
- Harkany T, Guzman M, Galve-Roperh I, Berghuis P, Devi LA, et al. The emerging functions of endocannabinoid signaling during CNS development. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28:83–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

