Protective effects of a Rhodiola crenulata extract and salidroside on hippocampal neurogenesis against streptozotocin-induced neural injury in the rat
- PMID: 22235318
- PMCID: PMC3250459
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029641
Protective effects of a Rhodiola crenulata extract and salidroside on hippocampal neurogenesis against streptozotocin-induced neural injury in the rat
Abstract
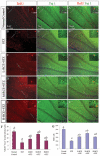
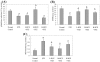
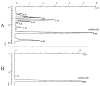
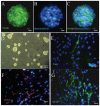
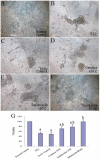
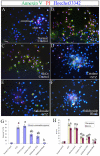
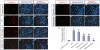
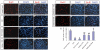
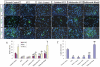
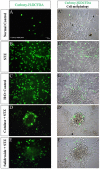
Previously we have demonstrated that a Rhodiola crenulata extract (RCE), containing a potent antioxidant salidroside, promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus of depressive rats. The current study was designed to further investigate the protective effect of the RCE on neurogenesis in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease (AD) induced by an intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin (STZ), and to determine whether this neuroprotective effect is induced by the antioxidative activity of salidroside. Our results showed that pretreatment with the RCE significantly improved the impaired neurogenesis and simultaneously reduced the oxidative stress in the hippocampus of AD rats. In vitro studies revealed that (1) exposure of neural stem cells (NSCs) from the hippocampus to STZ strikingly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, induced cell death and perturbed cell proliferation and differentiation, (2) hydrogen peroxide induced similar cellular activities as STZ, (3) pre-incubation of STZ-treated NSCs with catalase, an antioxidant, suppressed all these cellular activities induced by STZ, and (4) likewise, pre-incubation of STZ-treated NSCs with salidroside, also an antioxidant, suppressed all these activities as catalase: reduction of ROS levels and NSC death with simultaneous increases in proliferation and differentiation. Our findings indicated that the RCE improved the impaired hippocampal neurogenesis in the rat model of AD through protecting NSCs by its main ingredient salidroside which scavenged intracellular ROS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Ziabreva I, Perry E, Perry R, Minger SL, Ekonomou A, et al. Altered neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease. J Psychosom Res. 2006;61:311–316. - PubMed
-
- Mohapel P, Leanza G, Kokaia M, Lindvall O. Forebrain acetylcholine regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis and learning. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:939–946. - PubMed
-
- Grundke-Iqbal I, Tatebayashi Y, Li L, Haque N, Iqbal K. Abnormalities in neurogenesis in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:S563–S563.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

