Fractalkine and other chemokines in primary biliary cirrhosis
- PMID: 22235377
- PMCID: PMC3251911
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/102839
Fractalkine and other chemokines in primary biliary cirrhosis
Abstract
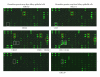
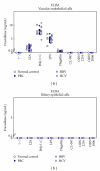
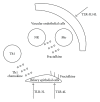
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is characterized by the autoimmune injury of small intrahepatic bile duct. On this basis, it has been suggested that the targeted biliary epithelial cells (BEC) play an active role in the perpetuation of autoimmunity by attracting immune cells via chemokine secretion. To address this issue, we challenged BEC using multiple toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands as well as autologous liver infiltrating mononuclear cells (LMNC) with subsequent measurement of BEC phenotype and chemokine production and LMNC chemotaxis by quantifying specific chemokines, specially CX3CL1 (fractalkine). We submit the hypothesis that BEC are in fact the innocent victims of the autoimmune injury and that the adaptive immune response is critical in PBC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biliary epithelial cells and primary biliary cirrhosis: the role of liver-infiltrating mononuclear cells.Hepatology. 2008 Mar;47(3):958-65. doi: 10.1002/hep.22102. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18181218
-
[Pathogenesis of biliary tract injury in primary biliary cirrhosis].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012;35(6):455-62. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012. PMID: 23291480 Review. Japanese.
-
CX3CL1 (fractalkine): a signpost for biliary inflammation in primary biliary cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2010 Feb;51(2):567-75. doi: 10.1002/hep.23318. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 19908209 Free PMC article.
-
Fractalkine and CX3CR1 are involved in the recruitment of intraepithelial lymphocytes of intrahepatic bile ducts.Hepatology. 2005 Mar;41(3):506-16. doi: 10.1002/hep.20582. Hepatology. 2005. PMID: 15726664
-
Innate immunity in the pathogenesis of cholangiopathy: a recent update.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2012 Dec;11(6):478-83. doi: 10.2174/187152812803589976. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22920631 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of novel retroviruses in chronic liver disease: assessing the link of human betaretrovirus with primary biliary cirrhosis.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2015 Feb;17(2):460. doi: 10.1007/s11908-014-0460-7. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2015. PMID: 25754451 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of Vδ1 T cells in peripheral blood and livers of patients with primary biliary cholangitis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Dec;186(3):347-355. doi: 10.1111/cei.12852. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27543908 Free PMC article.
-
Ongoing activation of autoantigen-specific B cells in primary biliary cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2014 Nov;60(5):1708-16. doi: 10.1002/hep.27313. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 25043065 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Chemokine/Chemokine Receptor Axes and NK Cell Tissue Localization during Diseases.Front Immunol. 2016 Oct 6;7:402. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00402. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27766097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK Cell Subtypes as Regulators of Autoimmune Liver Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:6903496. doi: 10.1155/2016/6903496. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27462349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harada K, Van De Water J, Leung PS, et al. In situ nucleic acid hybridization of cytokines in primary biliary cirrhosis: predominance of the Th1 subset. Hepatology. 1997;25(4):791–796. - PubMed
-
- Wu CT, Davis PA, Luketic VA, Gershwin ME. A review of the physiological and immunological functions of biliary epithelial cells: targets for primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and drug-induced ductopenias. Clinical and Developmental Immunology. 2004;11(3-4):205–213. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

