Cerebrovascular complications of diabetes: focus on stroke
- PMID: 22236022
- PMCID: PMC3741336
- DOI: 10.2174/187153012800493477
Cerebrovascular complications of diabetes: focus on stroke
Abstract
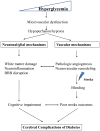
Cerebrovascular complications make diabetic patients 2-6 times more susceptible to a stroke event and this risk is magnified in younger individuals and in patients with hypertension and complications in other vascular beds. In addition, when patients with diabetes and hyperglycemia experience an acute ischemic stroke they are more likely to die or be severely disabled and less likely to benefit from the one FDA-approved therapy, intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Experimental stroke models have revealed that chronic hyperglycemia leads to deficits in cerebrovascular structure and function that may explain some of the clinical observations. Increased edema, neovascularization and protease expression as well as altered vascular reactivity and tone may be involved and point to potential therapeutic targets. Further study is needed to fully understand this complex disease state and the breadth of its manifestation in the cerebrovasculature.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. [Accessed on March 30, 2011];National diabetes fact sheet. Available from http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-statistics.jsp.
-
- Ehehalt S, Blumenstock G, Willasch AM, Hub R, Ranke MB, Neu A. Continuous rise in incidence of childhood Type 1 diabetes in Germany. Diabet Med. 2008;25(6):755–7. - PubMed
-
- Kumar P, Krishna P, Reddy SC, Gurappa M, Aravind SR, Munichoodappa C. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus and associated complications among children and young adults: results from Karnataka Diabetes Registry 1995–2008. J Indian Med Assoc. 2008;106(11):708–11. - PubMed
-
- Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. EURODIAB ACE Study Group. Lancet. 2000;355(9207):873–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

