Increased survival and reduced renal injury in MRL/lpr mice treated with a human Fcγ receptor II (CD32) peptide
- PMID: 22236212
- PMCID: PMC3372756
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03553.x
Increased survival and reduced renal injury in MRL/lpr mice treated with a human Fcγ receptor II (CD32) peptide
Abstract
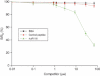
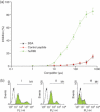
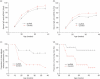
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem chronic inflammatory disease affecting many organs. The deposition in kidney tissue of immune complexes and their interaction with macrophages is thought to trigger the inflammatory response leading to glomerulonephritis. It has been demonstrated that inhibition of this interaction in murine models can alleviate the disease. Six synthetic peptides were derived from the membrane-proximal extracellular domain (EC2) of human Fcγ receptor II (huFcγRII). Of these, one peptide, huRII6, was shown to be a potent competitive inhibitor of IgG binding to recombinant FcγRII in vitro. To examine the possible therapeutic impact of huRII6 in vivo, this peptide, or a control, was given by subcutaneous injection to female MRL/lpr mice from weeks 7 to 36, resulting in an enhanced survival rate compared with control-treated animals and a reduction of proteinuria. Histopathological examination of the kidneys showed a reduction in deposition of immune complexes and preservation of structure. Such a functional peptide should prove useful for examining the role of IgG-FcγR interactions in experimental models of disease and may provide for the development of FcR-targeting drugs to treat autoimmune disorders.
© 2012 The Authors. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevention of systemic lupus erythematosus in MRL/lpr mice by administration of an immunoglobulin-binding peptide.Nat Biotechnol. 2000 Jul;18(7):735-9. doi: 10.1038/77296. Nat Biotechnol. 2000. PMID: 10888840
-
Fc receptor-independent development of autoimmune glomerulonephritis in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Feb;48(2):486-94. doi: 10.1002/art.10813. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12571859
-
Activated protein C attenuates systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice.J Immunol. 2011 Sep 15;187(6):3413-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101125. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21849682
-
Animal models of studying the pathogenesis of multi-organ tissue damage in lupus.Clin Immunol. 2024 Jun;263:110231. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.110231. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38692449 Review.
-
[Fcγ receptor and systemic autoimmune disease].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2011;34(1):1-7. doi: 10.2177/jsci.34.1. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2011. PMID: 21372507 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Identification of the Linear Fc-Binding Site on the Bovine IgG1 Fc Receptor (boFcγRIII) Using Synthetic Peptides.Vet Sci. 2024 Jan 8;11(1):24. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11010024. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38250930 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Core-Shell Microcapsule for Encapsulation and 3D Culture of Embryonic Stem Cells.J Mater Chem B. 2013;2013(7):1002-1009. doi: 10.1039/C2TB00058J. Epub 2012 Nov 23. J Mater Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23505611 Free PMC article.
-
The Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2014 Apr;5(2):205. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000205. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25133068 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cell-derived immunoglobulin G activates platelets by binding to platelet FcγRIIa.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 28;10(2):87. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1367-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30692520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Dixon FJ. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. - PubMed
-
- Reilly CM, Gilkeson GS. Use of genetic knockouts to modulate disease expression in a murine model of lupus, MRL/lpr mice. Immunol Res. 2002;25:143–53. - PubMed
-
- Ebling F, Hahn BH. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:392–403. - PubMed
-
- Mannik M. Pathophysiology of circulating immune complexes. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:783–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

