Immunolocalization of sprouty-1 and sprouty-2 in developing rat lung
- PMID: 22236546
- PMCID: PMC3270822
- DOI: 10.1159/000332215
Immunolocalization of sprouty-1 and sprouty-2 in developing rat lung
Abstract
Objective: Sprouty, a common antagonist of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and epidermal growth factor signaling, is a key player regulating tracheal branching and eye development in Drosophila. Four Sprouty homologs have been identified in vertebrates and all share a cysteine-rich region. However, the physiological function(s) of the individual Sprouty homologs is unknown. mRNA of Sprouty homologs is expressed during mouse lung development. In the present study, we investigated the immunolocalization of Sprouty proteins in rat lung at different stages of development.
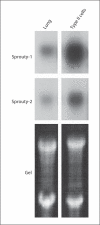
Methods: Rabbit antibodies were raised against peptides derived from rat Sprouty-1 and Sprouty-2 and were used in Western blot analysis to determine Sprouty distribution in subcellular fractions (pellets and supernatant centrifuged at 5,000 and 20,000 g) and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) from adult rat lungs or used in immunohistochemistry.
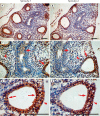
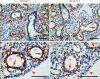
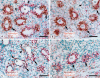
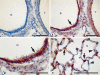
Results: Western blot analysis revealed a 30-kDa Sprouty-1 band and a 34-kDa Sprouty-2 band in the supernatant and pellet fractions centrifuged at 20,000 g. BAL contained a band of approximately 16 kDa with Sprouty-1 antibody derived from proteolytic fragmentation of Sprouty-1. In embryonic day (E) 14 and E16 lungs, Sprouty-1 and Sprouty-2 were expressed both in epithelial and peripheral mesenchymal cells. In adult rat lung, bronchiolar and alveolar type II epithelial cells showed staining for both Sprouty-1 and Sprouty-2. Sprouty-1 expression was also seen in alveolar type I epithelial cells.
Conclusion: In light of the proximity of the distribution of Sprouty to that of FGF-10 (peripheral mesenchyme) and its receptor FGFR2IIIb (distal tubular epithelium) in lung development, and the finding that FGF-9, which is expressed in mesothelial cells, upregulates FGF-10, it appears that Sprouty expression in epithelial and mesenchymal cells during branching morphogenesis is closely related to signaling by FGF-9 and FGF-10.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures






References
-
- Casci T, Vinos J, Freeman M. Sprouty, an intracellular inhibitor of ras signaling. Cell. 1999;96:655–665. - PubMed
-
- Hacohen N, Kramer S, Sutherland D, Hiromi Y, Krasnow MA. Sprouty encodes a novel antagonist of FGF signaling that patterns apical branching of the Drosophila airways. Cell. 1998;92:253–263. - PubMed
-
- Kramer S, Okabe M, Hacohen N, Krasnow MA, Hiromi Y. Sprouty: a common antagonist of FGF and EGF signaling pathways in Drosophila. Development. 1999;126:2515–2525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

