Selective optogenetic stimulation of cholinergic axons in neocortex
- PMID: 22236708
- PMCID: PMC3331667
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00870.2011
Selective optogenetic stimulation of cholinergic axons in neocortex
Abstract
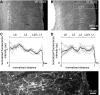
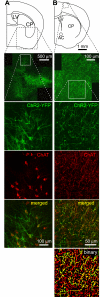
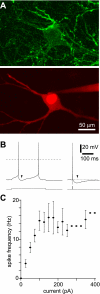
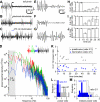
Acetylcholine profoundly affects neocortical function, being involved in arousal, attention, learning, memory, sensory and motor function, and plasticity. The majority of cholinergic afferents to neocortex are from neurons in nucleus basalis. Nucleus basalis also contains projecting neurons that release other transmitters, including GABA and possibly glutamate. Hence, electrical stimulation of nucleus basalis evokes the release of a mixture of neurotransmitters in neocortex, and this lack of selectivity has impeded research on cholinergic signaling in neocortex. We describe a method for the selective stimulation of cholinergic axons in neocortex. We used the Cre-lox system and a viral vector to express the light-activated protein channelrhodopsin-2 in cholinergic neurons in nucleus basalis and their axons in neocortex. Labeled neurons depolarized on illumination with blue light but were otherwise unchanged. In anesthetized mice, illumination of neocortex desynchronized the local field potential, indicating that light evoked release of ACh. This novel technique will enable many new studies of the cellular, network, and behavioral physiology of ACh in neocortex.
Figures





References
-
- Aravanis AM, Wang LP, Zhang F, Meltzer LA, Mogri MZ, Schneider MB, Deisseroth K. An optical neural interface: in vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. J Neural Eng 4: S143–S156, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Avendanǒ C, Umbriaco D, Dykes RW, Descarries L. Acetylcholine innervation of sensory and motor neocortical areas in adult cat: a choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemical study. J Chem Neuroanat 11: 113–130, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Ayling OG, Harrison TC, Boyd JD, Goroshkov A, Murphy TH. Automated light-based mapping of motor cortex by photoactivation of channelrhodopsin-2 transgenic mice. Nat Methods 6: 219–224, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Berg RW, Friedman B, Schroeder LF, Kleinfeld D. Activation of nucleus basalis facilitates cortical control of a brain stem motor program. J Neurophysiol 94: 699–711, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

