DNA damage induces reactive oxygen species generation through the H2AX-Nox1/Rac1 pathway
- PMID: 22237206
- PMCID: PMC3270268
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.134
DNA damage induces reactive oxygen species generation through the H2AX-Nox1/Rac1 pathway
Abstract
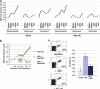
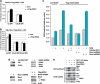
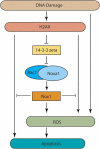
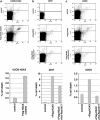
The DNA damage response (DDR) cascade and ROS (reactive oxygen species) signaling are both involved in the induction of cell death after DNA damage, but a mechanistic link between these two pathways has not been clearly elucidated. This study demonstrates that ROS induction after treatment of cells with neocarzinostatin (NCS), an ionizing radiation mimetic, is at least partly mediated by increasing histone H2AX. Increased levels of ROS and cell death induced by H2AX overexpression alone or DNA damage leading to H2AX accumulation are reduced by treating cells with the antioxidant N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC), the NADP(H) oxidase (Nox) inhibitor DPI, expression of Rac1N17, and knockdown of Nox1, but not Nox4, indicating that induction of ROS by H2AX is mediated through Nox1 and Rac1 GTPase. H2AX increases Nox1 activity partly by reducing the interaction between a Nox1 activator NOXA1 and its inhibitor 14-3-3zeta. These results point to a novel role of histone H2AX that regulates Nox1-mediated ROS generation after DNA damage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of Rac1 in activation of multicomponent Nox1- and Nox3-based NADPH oxidases.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(6):2160-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2160-2174.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507994 Free PMC article.
-
Nox1-dependent reactive oxygen generation is regulated by Rac1.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 30;281(26):17718-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512751200. Epub 2006 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16636067
-
Regulation of Nox1 activity via protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of NoxA1 and 14-3-3 binding.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 30;282(48):34787-800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704754200. Epub 2007 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17913709
-
Organizers and activators: Cytosolic Nox proteins impacting on vascular function.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Aug;109:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.03.017. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28336130 Review.
-
Metabolic Rewiring in the Face of Genomic Assault: Integrating DNA Damage Response and Cellular Metabolism.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 23;15(2):168. doi: 10.3390/biom15020168. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of NADPH oxidase alleviates germ cell apoptosis and ER stress during testicular ischemia reperfusion injury.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Aug;27(8):2174-2184. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.04.024. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32714044 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the role of bisphenol A (BPA) in genomic instability.NAR Cancer. 2024 Sep 24;6(3):zcae038. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae038. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39319028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deregulation of DNA damage response pathway by intercellular contact.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16246-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.337212. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22431734 Free PMC article.
-
ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer.Redox Biol. 2019 Jul;25:101084. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.101084. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30612957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Balance-DDR-miRNA Triangle: Relevance in Genome Stability and Stress Responses in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Aug 2;10:989. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00989. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31428113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bassing CH, Alt FW. The cellular response to general and programmed DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair. 2004;3:781–796. - PubMed
-
- Zhou BB, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 2000;408:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Capetillo O, Lee A, Nussenzweig M, Nussenzweig A. H2AX: the histone guardian of the genome. DNA Repair. 2004;3:959–967. - PubMed
-
- Stucki M, Clapperton JA, Mohammad D, Yaffe MB, Smerdon SJ, Jackson SP. MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated histone H2AX to regulate cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell. 2005;123:1213–1226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

