A novel radioresistant mechanism of galectin-1 mediated by H-Ras-dependent pathways in cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 22237208
- PMCID: PMC3270263
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.120
A novel radioresistant mechanism of galectin-1 mediated by H-Ras-dependent pathways in cervical cancer cells
Abstract
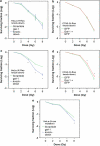
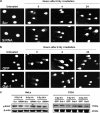
Galectin-1 is a lectin recognized by galactoside-containing glycoproteins, and is involved in cancer progression and metastasis. The role of galectin-1 in radiosensitivity has not previously been investigated. Therefore, this study tests whether galectin-1 is involved in the radiosensitivity mediated by the H-Ras signaling pathway using cervical carcinoma cell lines. A knockdown of galectin-1 expression in HeLa cells decreased clonogenic survival following irradiation. The clonogenic survival increased in both HeLa and C33A cells with galectin-1 overexpression. The overexpression or knockdown of galectin-1 did not alter radiosensitivity, whereas H-Ras was silenced in both cell lines. Whereas K-Ras was knocked down, galectin-1 restored the radiosensitivity in HeLa cells and C33A cells. The knockdown of galectin-1 increased the high-dose radiation-induced cell death of HeLa cells transfected by constitutively active H-Ras. The knockdown of galectin-1 inhibited the radiation-induced phosphorylation of Raf-1 and ERK in HeLa cells. Overexpression of galectin-1 enhanced the phosphorylation of Raf-1 and ERK in C33A cells following irradiation. Galectin-1 decreased the DNA damage detected using comet assay and γ-H2AX in both cells following irradiation. These findings suggest that galectin-1 mediates radioresistance through the H-Ras-dependent pathway involved in DNA damage repair.
Figures



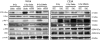

Similar articles
-
Radiation-induced increase in cell migration and metastatic potential of cervical cancer cells operates via the K-Ras pathway.Am J Pathol. 2012 Feb;180(2):862-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.018. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22138581
-
Galectin-1 augments Ras activation and diverts Ras signals to Raf-1 at the expense of phosphoinositide 3-kinase.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 4;277(40):37169-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205698200. Epub 2002 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12149263
-
Overexpression of galectin-3 enhances migration of colon cancer cells related to activation of the K-Ras-Raf-Erk1/2 pathway.J Gastroenterol. 2013 Mar;48(3):350-9. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0663-3. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23015305
-
DNA-PKcs plays a dominant role in the regulation of H2AX phosphorylation in response to DNA damage and cell cycle progression.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 6;11:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-18. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20205745 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-1 links tumor hypoxia and radiotherapy.Glycobiology. 2014 Oct;24(10):921-5. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu062. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24973253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systems-level effects of ectopic galectin-7 reconstitution in cervical cancer and its microenvironment.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 24;16(1):680. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2700-8. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27558259 Free PMC article.
-
Amifostine alleviates radiation-induced lethal small bowel damage via promotion of 14-3-3σ-mediated nuclear p53 accumulation.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 30;5(20):9756-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2386. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25230151 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation leads to enhanced radiosensitivity through induction of apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells.J Biophotonics. 2017 Dec;10(12):1732-1742. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700004. Epub 2017 May 2. J Biophotonics. 2017. PMID: 28464474 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein-1 (MRP-1)-dependent Glutathione Disulfide (GSSG) Efflux as a Critical Survival Factor for Oxidant-enriched Tumorigenic Endothelial Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6;291(19):10089-103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.688879. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26961872 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Galectin-1 but Not Galectin-3 in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinoma After Radiation Therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 23;12:834749. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.834749. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang EY, Wang CJ, Chen HC, Fang FM, Huang YJ, Wang CY, et al. Multivariate analysis of para-aortic lymph node recurrence after definitive radiotherapy for stage IB-IVA squamous cell carcinoma of uterine cervix. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72:834–842. - PubMed
-
- Hertlein L, Lenhard M, Kirschenhofer A, Kahlert S, Mayr D, Burges A, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy in advanced cervical cancer: a retrospective study with five patients. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2011;283:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Kurtz JE, Hardy-Bessard AC, Deslandres M, Lavau-Denes S, Largillier R, Roemer-Becuwe C, et al. Cetuximab, topotecan and cisplatin for the treatment of advanced cervical cancer: a phase II GINECO trial. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Goncalves A, Fabbro M, Lhommé C, Gladieff L, Extra JM, Floquet A, et al. A phase II trial to evaluate gefitinib as second- or third-line treatment in patients with recurring locoregionally advanced or metastatic cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;108:42–46. - PubMed
-
- Gaffney DK, Winter K, Dicker AP, Miller B, Eifel PJ, Ryu J, et al. A Phase II study of acute toxicity for Celebrex (celecoxib) and chemoradiation in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer: primary endpoint analysis of RTOG 0128. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:104–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

