Efficacy and safety of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and poor risk features
- PMID: 22237457
- PMCID: PMC11824590
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-012-1148-8
Efficacy and safety of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and poor risk features
Abstract
Background: Temsirolimus is a standard of care in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) with poor risk factors. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) remains poorly defined in this setting.
Methods: Records of our center were examined to identify patients with mRCC and 3 or more poor prognosis factors, as determined in the Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (ARCC) trial, who had been treated with VEGFR TKIs. Their baseline characteristics, radiologic response, adverse events, and survival status were assessed.
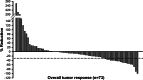
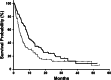
Results: The 88 patients who met our inclusion criteria had a median age of 56 years (range 17-83 years). We observed clear cell histology in 71 (81%) patients, and 52 (59%) underwent prior nephrectomy. Seventy-six patients (86%) were treated with sunitinib and 10 (11%) with sorafenib. Of 85 patients with measurable lesions, 19 (22%) showed objective response, with disease control achieved in 49 (56%). At a median follow-up of 29.6 months, the median time to progression was 5.0 months (95% CI, 3.5-6.5 months) and the median overall survival (OS) was 9.3 months (95% CI, 7.1-11.5 months). Neutrophil count (>ULN), bone metastasis, and lymph node metastasis were independent prognostic factors for OS, whereas prior nephrectomy was not.
Conclusions: VEGFR TKIs, especially sunitinib, are active and tolerated by mRCC patients with poor risk features.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to be declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bevacizumab, sorafenib tosylate, sunitinib and temsirolimus for renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jan;14(2):1-184, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta14020. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20028613
-
Combination of Temsirolimus and tyrosine kinase inhibitors in renal carcinoma and endothelial cell lines.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun;138(6):907-16. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1162-x. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22322364 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of arterial thromboembolic events with sunitinib and sorafenib: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.J Clin Oncol. 2010 May 1;28(13):2280-5. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.2757. Epub 2010 Mar 29. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20351323
-
First-line therapy for treatment-naive patients with advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of published randomized controlled trials.Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Jun;27(5):383-97. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000335. Anticancer Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26886011
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing the Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Different Systemic Treatments for Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):426-436. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27939075
Cited by
-
First-Line Treatments for Poor-Prognosis Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Experts' Prescribing Practices and Systematic Literature Review.Clin Drug Investig. 2016 May;36(5):389-99. doi: 10.1007/s40261-016-0384-0. Clin Drug Investig. 2016. PMID: 26945986
-
Current status of targeted therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma.Korean J Urol. 2012 Apr;53(4):217-28. doi: 10.4111/kju.2012.53.4.217. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Korean J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22536463 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment neutrophil count in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jun 10;11:5365-5374. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S199849. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31354345 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with extensive sarcomatoid component.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 May;139(5):817-27. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1386-4. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23397357 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches in Surgical and Immunotherapy-Based Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma with Tumor Thrombus.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 13;11(1):204. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010204. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36672712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beck J, Procopio G, Bajetta E, Keilholz U, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Bokemeyer C, Bracarda S, Richel DJ, Staehler M, Strauss UP, Mersmann S, Burock K, Escudier B (2011) Final results of the European advanced renal cell carcinoma sorafenib (EU-ARCCS) expanded-access study: a large open-label study in diverse community settings. Ann Oncol 22(8):1812–1823 - PubMed
-
- Britten CD, Kabbinavar F, Hecht JR, Bello CL, Li J, Baum C, Slamon D (2008) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of sunitinib administered daily for 2 weeks, followed by a 1-week off period. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61(3):515–524. doi:10.1007/s00280-007-0498-4 - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK, Xie W, Kollmannsberger C, North S, Knox JJ, Lampard JG, McDermott DF, Rini BI, Heng DY (2011) The impact of cytoreductive nephrectomy on survival of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving vascular endothelial growth factor targeted therapy. J Urol 185(1):60–66. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.09.012 - PubMed
-
- Cohen HT, McGovern FJ (2005) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353(23):2477–2490. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043172 - PubMed
-
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

