Tune it down to live it up? Rapid, nongenomic effects of cortisol on the human brain
- PMID: 22238097
- PMCID: PMC6621076
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2384-11.2012
Tune it down to live it up? Rapid, nongenomic effects of cortisol on the human brain
Abstract
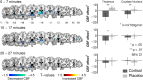
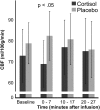
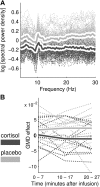
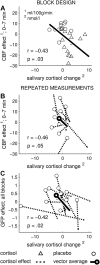
The stress hormone cortisol acts on the brain, supporting adaptation and time-adjusted coping processes. Whereas previous research has focused on slow emerging, genomic effects of cortisol, we addressed the rapid, nongenomic cortisol effects on in vivo neuronal activity in humans. Three independent placebo-controlled studies in healthy men were conducted. We observed changes in CNS activity within 15 min after intravenous administration of a physiological dose of 4 mg of cortisol (hydrocortisone). Two of the studies demonstrated a rapid bilateral thalamic perfusion decrement using continuous arterial spin labeling. The third study revealed rapid, cortisol-induced changes in global signal strength and map dissimilarity of the electroencephalogram. Our data demonstrate that a physiological concentration of cortisol profoundly affects the functioning and perfusion of the human brain in vivo via a rapid, nongenomic mechanism. The changes in neuronal functioning suggest that cortisol acts on the thalamic relay of background as well as on task-specific sensory information, allowing focus and facilitation of adaptation to challenges.
Figures
References
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Reduced transit-time sensitivity in noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of human cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:1236–1249. - PubMed
-
- Bell AJ, Sejnowski TJ. An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput. 1995;7:1129–1159. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield P. Fourier analysis of time series: an introduction. New York: Wiley; 1976.
-
- Brunia CH. Neural aspects of anticipatory behavior. Acta Psychol (Amst) 1999;101:213–242. - PubMed
-
- Chatrian GE, Lettich E, Nelson PL. Modified nomenclature for the “10%” electrode system. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1988;5:183–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
