Aβ delays fibrin clot lysis by altering fibrin structure and attenuating plasminogen binding to fibrin
- PMID: 22238323
- PMCID: PMC3321860
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-389668
Aβ delays fibrin clot lysis by altering fibrin structure and attenuating plasminogen binding to fibrin
Abstract
Alzheimer disease is characterized by the presence of increased levels of the β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) in the brain parenchyma and cerebral blood vessels. This accumulated Aβ can bind to fibrin(ogen) and render fibrin clots more resistant to degradation. Here, we demonstrate that Aβ(42) specifically binds to fibrin and induces a tighter fibrin network characterized by thinner fibers and increased resistance to lysis. However, Aβ(42)-induced structural changes cannot be the sole mechanism of delayed lysis because Aβ overlaid on normal preformed clots also binds to fibrin and delays lysis without altering clot structure. In this regard, we show that Aβ interferes with the binding of plasminogen to fibrin, which could impair plasmin generation and fibrin degradation. Indeed, plasmin generation by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), but not streptokinase, is slowed in fibrin clots containing Aβ(42), and clot lysis by plasmin, but not trypsin, is delayed. Notably, plasmin and tPA activities, as well as tPA-dependent generation of plasmin in solution, are not decreased in the presence of Aβ(42). Our results indicate the existence of 2 mechanisms of Aβ(42) involvement in delayed fibrinolysis: (1) through the induction of a tighter fibrin network composed of thinner fibers, and (2) through inhibition of plasmin(ogen)-fibrin binding.
Figures
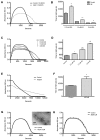
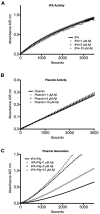
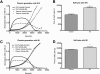




Comment in
-
Aβ and C(lot), but not D(egradation).Blood. 2012 Apr 5;119(14):3196-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-406660. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22493214
References
-
- de la Torre JC. Alzheimer disease as a vascular disorder: nosological evidence. Stroke. 2002;33(4):1152–1162. - PubMed
-
- de la Torre JC. Is Alzheimer's disease a neurodegenerative or a vascular disorder? Data, dogma, and dialectics. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3(3):184–190. - PubMed
-
- Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(5):347–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

