FLNA genomic rearrangements cause periventricular nodular heterotopia
- PMID: 22238415
- PMCID: PMC3280053
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824365e4
FLNA genomic rearrangements cause periventricular nodular heterotopia
Abstract
Objective: To identify copy number variant (CNV) causes of periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) in patients for whom FLNA sequencing is negative.
Methods: Screening of 35 patients from 33 pedigrees on an Affymetrix 6.0 microarray led to the identification of one individual bearing a CNV that disrupted FLNA. FLNA-disrupting CNVs were also isolated in 2 other individuals by multiplex ligation probe amplification. These 3 cases were further characterized by high-resolution oligo array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), and the precise junctional breakpoints of the rearrangements were identified by PCR amplification and sequencing.
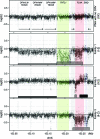
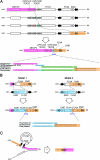
Results: We report 3 cases of PNH caused by nonrecurrent genomic rearrangements that disrupt one copy of FLNA. The first individual carried a 113-kb deletion that removes all but the first exon of FLNA. A second patient harbored a complex rearrangement including a deletion of the 3' end of FLNA accompanied by a partial duplication event. A third patient bore a 39-kb deletion encompassing all of FLNA and the neighboring gene EMD. High-resolution oligo array CGH of the FLNA locus suggests distinct molecular mechanisms for each of these rearrangements, and implicates nearby low copy repeats in their pathogenesis.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that FLNA is prone to pathogenic rearrangements, and highlight the importance of screening for CNVs in individuals with PNH lacking FLNA point mutations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FLNA genomic rearrangements in a 391 French bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia cohort: prevalence and phenotypic correlations.J Med Genet. 2025 Mar 20;62(4):227-230. doi: 10.1136/jmg-2024-110336. J Med Genet. 2025. PMID: 39779312
-
Filamin A mutations cause periventricular heterotopia with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Neurology. 2005 Jan 25;64(2):254-62. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000149512.79621.DF. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 15668422
-
Bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia in France: frequency of mutations in FLNA, phenotypic heterogeneity and spectrum of mutations.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009 Dec;80(12):1394-8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2008.162263. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19917821
-
Periventricular nodular heterotopias is associated with mutation at the FLNA locus-a case history and a literature review.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Jul 8;23(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04161-4. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37422633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trouble making the first move: interpreting arrested neuronal migration in the cerebral cortex.Trends Neurosci. 2008 Feb;31(2):54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.11.009. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Trends Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18201775 Review.
Cited by
-
Clues beyond the lung: an unusual diagnosis in an infant with chronic lung disease.Breathe (Sheff). 2020 Mar;16(1):190319. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0319-2019. Breathe (Sheff). 2020. PMID: 32494305 Free PMC article.
-
Large palindromes on the primate X Chromosome are preserved by natural selection.Genome Res. 2021 Aug;31(8):1337-1352. doi: 10.1101/gr.275188.120. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Genome Res. 2021. PMID: 34290043 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of FLNA attenuating the migration of abdominal muscles contributed to Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS) in a family with recurrent miscarriage.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 May;11(5):e2145. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2145. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023. PMID: 36734119 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the impact of uncharacterized inversions in the human genome by droplet digital PCR.Genome Res. 2020 May;30(5):724-735. doi: 10.1101/gr.255273.119. Epub 2020 May 18. Genome Res. 2020. PMID: 32424072 Free PMC article.
-
Periventricular nodular heterotopia in 22q11.2 deletion and frontal lobe migration.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Sep 23;5(11):1314-1322. doi: 10.1002/acn3.641. eCollection 2018 Nov. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30480026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ekşioğlu YZ, Scheffer IE, Cardenas P, et al. Periventricular heterotopia: an X-linked dominant epilepsy locus causing aberrant cerebral cortical development. Neuron 1996;16:77–87 - PubMed
-
- Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Ekşioğlu YZ, et al. Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron 1998;21:1315–1325 - PubMed
-
- Guerrini R, Mei D, Sisodiya S, et al. Germline and mosaic mutations of FLN1 in men with periventricular heterotopia. Neurology 2004;63:51–56 - PubMed
-
- Parrini E, Ramazzotti A, Dobyns WB, et al. Periventricular heterotopia: phenotypic heterogeneity and correlation with Filamin A mutations. Brain 2006;129:1892–1906 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
