Comparison of commercial extraction systems and PCR assays for quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in whole blood
- PMID: 22238432
- PMCID: PMC3318550
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05593-11
Comparison of commercial extraction systems and PCR assays for quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in whole blood
Abstract
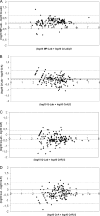
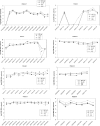
The automation of DNA extraction and the use of commercial quantitative real-time PCR assays could help obtain more reliable results for the quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA loads (EBV VL). This study compared two automated extraction platforms and two commercial PCRs for measurement of EBV VL in 10 EBV specimens from Quality Control for Molecular Diagnostics (QCMD) and in 200 whole-blood (WB) specimens from transplant (n = 137) and nontransplant (n = 63) patients. The WB specimens were extracted using the QIAcube or MagNA Pure instrument; VL were quantified with the EBV R-gene quantification kit (Argene) or the artus EBV RG PCR kit (Qiagen) on the Rotor-Gene 6000 real-time analyzer; and the results were compared with those of a laboratory-developed PCR. DNA was extracted from the QCMD specimens by use of the QIAamp DNA minikit and was quantified by the three PCR assays. The extraction platforms and the PCR assays showed good correlation (R, >0.9; P, <0.0001), but as many as 10% discordant results were observed, mostly for low viral loads (<3 log(10) copies/ml), and standard deviations reached as high as 0.49 log(10) copy/ml. In WB but not in QCMD samples, Argene PCR tended to give higher VL values than artus PCR or the laboratory-developed PCR (mean difference for the 200 WB VL, -0.42 or -0.36, respectively). In conclusion, the two automated extraction platforms and the two PCRs provided reliable and comparable VL results, but differences greater than 0.5 log(10) copy/ml remained between the two commercial PCRs after common DNA extraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance of the Real-Q EBV Quantification Kit for Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Quantification in Whole Blood.Ann Lab Med. 2017 Mar;37(2):147-150. doi: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.147. Ann Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 28029001 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Epstein-Barr virus R-gene quantification kit in whole blood with different extraction methods and PCR platforms.J Mol Diagn. 2008 Jan;10(1):78-84. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2008.070054. Epub 2007 Dec 28. J Mol Diagn. 2008. PMID: 18165270 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of six different specimen types for Epstein-Barr viral load quantification in peripheral blood of pediatric patients after heart transplantation or after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Clin Virol. 2012 Mar;53(3):186-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2011.11.010. Epub 2011 Dec 17. J Clin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22182950
-
Using Epstein-Barr viral load assays to diagnose, monitor, and prevent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Apr;23(2):350-66. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00006-09. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20375356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic testing in Epstein-Barr virus infection.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2001 Sep;39(9):789-94. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2001.130. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2001. PMID: 11601674 Review.
Cited by
-
Multicenter Evaluation of Whole-Blood Epstein-Barr Viral Load Standardization Using the WHO International Standard.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Jul;54(7):1746-1750. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03336-15. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27076661 Free PMC article.
-
Automated quantification of Epstein-Barr virus in whole blood for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders monitoring.Virol J. 2020 Feb 3;17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-1285-7. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32014036 Free PMC article.
-
Serum survivin and vascular endothelial growth factor in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: implications for a potential new prognostic indicator.Haematologica. 2015 Mar;100(3):e106-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.116087. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25480498 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Performance of the Real-Q EBV Quantification Kit for Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Quantification in Whole Blood.Ann Lab Med. 2017 Mar;37(2):147-150. doi: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.147. Ann Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 28029001 Free PMC article.
-
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease after lung transplantation.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:430209. doi: 10.1155/2013/430209. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23533455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbate I, et al. 2011. Multicenter comparative study of Epstein-Barr virus DNA quantification for virological monitoring in transplanted patients. J. Clin. Virol. 50:224–229 - PubMed
-
- Ahsanuddin AN, Standish MC, Caliendo AM, Hill CE, Nolte FS. 2008. Validation of an Epstein-Barr viral load assay using the QIAGEN Artus EBV TM PCR analyte-specific reagent. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 130:865–869 - PubMed
-
- Brengel-Pesce K, et al. 2002. Routine use of real-time quantitative PCR for laboratory diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infections. J. Med. Virol. 66:360–369 - PubMed
-
- De Paoli P, Pratesi C, Bortolin MT. 2007. The Epstein Barr virus DNA levels as a tumor marker in EBV-associated cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 133:809–815 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

