Recent advances in direct C-H arylation: Methodology, selectivity and mechanism in oxazole series
- PMID: 22238536
- PMCID: PMC3252862
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.7.187
Recent advances in direct C-H arylation: Methodology, selectivity and mechanism in oxazole series
Abstract
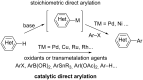
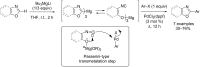
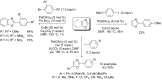
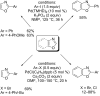
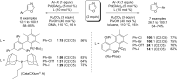
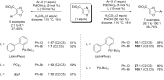
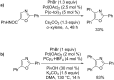
Catalytic direct (hetero)arylation of (hetero)arenes is an attractive alternative to traditional Kumada, Stille, Negishi and Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions, notably as it avoids the prior preparation and isolation of (hetero)arylmetals. Developments of this methodology in the oxazole series are reviewed in this article. Methodologies, selectivity, mechanism and future aspects are presented.
Keywords: ate complex; catalytic direct arylation; mechanism; oxazole; selectivity; transition-metal catalysis.
Figures
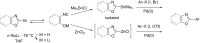



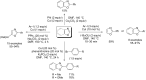
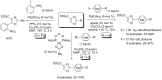
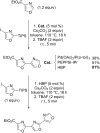
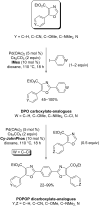


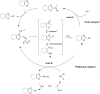

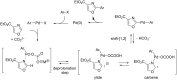

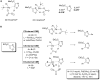
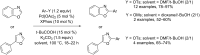
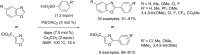

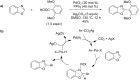
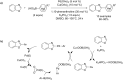
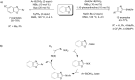



References
-
- Negishi E, de Meijere A, editors. Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 2002.
-
- de Meijere A, Diederich F, editors. Metal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions. 2nd ed. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
