Replication-independent expression of anti-apoptosis marker genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells infected with the wild-type HIV-1 and reverse transcriptase variants
- PMID: 22239233
- PMCID: PMC3271366
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2011.0057
Replication-independent expression of anti-apoptosis marker genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells infected with the wild-type HIV-1 and reverse transcriptase variants
Abstract
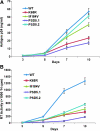
Clinical trials with highly-active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) have shown that a substantial number of patients continue to show a decrease in viral load and/or increase or stable CD4(+) T-cell numbers even in the presence of multidrug resistant (MDR) viruses. We compared replication capacity (RC) and expression of anti-apoptosis marker genes (AAMGs) in human peripheral blood mononuclear (PBM) cells infected with NL4-3 (wild-type; WT) and mutant viruses. Replication kinetics assays showed a significant decrease in RC of all mutant viruses in comparison to the WT virus. The viruses containing patient-derived MDR RT without the K65R mutation (PSD5.2) replicated efficiently in comparison to the viruses with MDR RT containing the K65R mutation (PSD5.1), or the single mutations K65R and M184V. Compared with WT, a significant decrease in RCs of viruses: K65R (RC=0.39±0.02; p≤0.0001), M184V (RC=0.72±0.04; p≤0.0001), PSD5.1 (RC=0.32±0.04; p≤0.0001), and PSD5.2 (RC=0.90±0.04; p=0.002) was observed on day 10. RT-PCR-based apoptosis array was performed on total cellular RNA. Recombinant virus PSD5.2 showed a 1.5- to 6-fold upregulation in 8 AAMGs (AKT1, BAG3, BCL2A1, BFAR, BIRC2, BNIP1, BNIP3, and CFLAR) on day 1 and day 7 post-infection with respect to WT virus. PSD5.1 showed upregulation of only one gene (BAG1) on day 1 (1.75-fold) and day 7 (1.97-fold). Point mutant K65R showed a 1.5- to 4-fold upregulation of six AAMGs on day 7. Viruses with the M184V mutation showed upregulation of only one gene (BAG1). These observations indicate that the upregulation of specific AAMGs may not be dependent on the RCs of HIV-I variants, and that the possible interaction among mutated RT residues and viral and/or host proteins may induce CD4(+) T-cell-protective anti-apoptosis proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Anand AR. Ganju RK. HIV-1 gp120-mediated apoptosis of T cells is regulated by the membrane tyrosine phosphatase CD45. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:12289–12299. - PubMed
-
- Ameisen JC. Estaquier J. Idziorek T. Bels F. The relevance of apoptosis to AIDS pathogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Badley AD. Pilon AA. Landay A. Lynch DH. Mechanisms of HIV-associated lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood. 2000;96:2951–2964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

