Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy
- PMID: 22239438
- PMCID: PMC3291787
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.2011.648617
Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy
Abstract
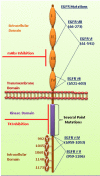
Introduction: Cancer is a devastating disease; however, several therapeutic advances have recently been made, wherein EGFR and its family members have emerged as useful biomarkers and therapeutic targets. EGFR, a transmembrane glycoprotein is a member of the ERBB receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily. EGFR binds to its cognate ligand EGF, which further induces tyrosine phosphorylation and receptor dimerization with other family members leading to enhanced uncontrolled proliferation. Several anti-EGFR therapies such as monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been developed, which has enabled clinicians to identify and treat specific patient cohorts.
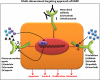
Areas covered: This review covers the basic mechanism of EGFR activation and the role of EGFR signaling in cancer progression. Furthermore, current developments made toward targeting the EGFR signaling pathway for the treatment of epithelial cancers and a summary of the various anti-EGFR therapeutic agents that are currently in use are also presented in this review.
Expert opinion: EGFR signaling is a part of a complex network that has been the target of effective cancer therapies. However, a further understanding of the system is required to develop an effective anticancer regimen. A combination therapy that comprises an anti-EGFR and a chemotherapeutic/chemopreventive agent will exhibit a multi-pronged approach that can be developed into a highly attractive and specific molecular oriented remedy.
Figures


References
-
- Grandis JR, Sok JC. Signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor during the development of malignancy. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;102:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Wells A. EGF receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:637–43. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson KM, Berger MB, Mendrola JM, et al. EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol Cell. 2003;11:507–17. - PubMed
-
- Ogiso H, Ishitani R, Nureki O, et al. Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell. 2002;110:775–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
