An integrative variant analysis suite for whole exome next-generation sequencing data
- PMID: 22239737
- PMCID: PMC3292476
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-8
An integrative variant analysis suite for whole exome next-generation sequencing data
Abstract
Background: Whole exome capture sequencing allows researchers to cost-effectively sequence the coding regions of the genome. Although the exome capture sequencing methods have become routine and well established, there is currently a lack of tools specialized for variant calling in this type of data.
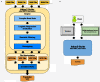
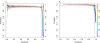
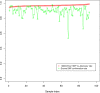
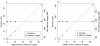
Results: Using statistical models trained on validated whole-exome capture sequencing data, the Atlas2 Suite is an integrative variant analysis pipeline optimized for variant discovery on all three of the widely used next generation sequencing platforms (SOLiD, Illumina, and Roche 454). The suite employs logistic regression models in conjunction with user-adjustable cutoffs to accurately separate true SNPs and INDELs from sequencing and mapping errors with high sensitivity (96.7%).
Conclusion: We have implemented the Atlas2 Suite and applied it to 92 whole exome samples from the 1000 Genomes Project. The Atlas2 Suite is available for download at http://sourceforge.net/projects/atlas2/. In addition to a command line version, the suite has been integrated into the Genboree Workbench, allowing biomedical scientists with minimal informatics expertise to remotely call, view, and further analyze variants through a simple web interface. The existing genomic databases displayed via the Genboree browser also streamline the process from variant discovery to functional genomics analysis, resulting in an off-the-shelf toolkit for the broader community.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

