An ecological model using promotores de salud to prevent cardiovascular disease on the US-Mexico border: the HEART project
- PMID: 22239750
- PMCID: PMC3310145
- DOI: 10.5888/pcd9.110100
An ecological model using promotores de salud to prevent cardiovascular disease on the US-Mexico border: the HEART project
Abstract
Background: To address cardiovascular disease risk factors among Hispanics, a community model of prevention requires a comprehensive approach to community engagement. The objectives of our intervention were to reduce cardiovascular disease risk factors in Hispanics living in 2 low-income areas of El Paso, Texas, and to engage the community in a physical activity and nutrition intervention.
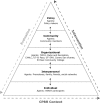
Methods: Drawing on lessons learned in phase 1 (years 2005-2008) of the HEART Project, we used an iterative, community-based process to develop an intervention based on an ecological framework. New community partners were introduced and community health workers delivered several elements of the intervention, including the curriculum entitled "Mi Corazón, Mi Comunidad" ("MiCMiC" [My Heart, My Community]). We received feedback from the project's Community Health Academy and Leadership Council throughout the development process and established a policy agenda that promotes integration of community health workers into the local and state workforce.
Outcome: Collaboration with 2 new community partners, the YWCA and the Department of Parks and Recreation, were instrumental in the process of community-based participatory research. We enrolled 113 participants in the first cohort; 78% were female, and the mean age was 41 years. More than 50% reported having no health insurance coverage. Seventy-two (60%) participants attended 1 or more promotora-led Su Corazón, Su Vida sessions, and 74 (62%) participants attended 1 or more of the 15 exercise classes.
Interpretation: HEART phase 2 includes a multilevel ecological model to address cardiovascular disease risk among Hispanics. Future similarly targeted initiatives can benefit from an ecological approach that also embraces the promotora model.
Figures
References
-
- Border lives: health status in the United States-Mexico border region. United States-Mexico Border Health Commission, 2010. [Accessed October 12, 2011]. http://www.borderhealth.org/extranet/files/file_1689.pdf .
-
- Staten L, Scheu L, Bronson D, Pena V, Elenes J. Pasos Adelante: the effectiveness of a community-based chronic disease prevention program. Prev Chronic Dis. 2005;2(1):Icon indicating a special focus articleA18. http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2005/jan/04_0075.htm . - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balcázar H, Alvarado M, Hollen ML, Gonzalez-Cruz Y, Hughes O, Vazquez E, Lykens K. Salud Para Su Corazón-NCLR: a comprehensive promotora outreach program to promote heart healthy behaviors among Hispanics. Health Promot Pract. 2006;7(1):68–77. - PubMed
-
- Balcázar H, Rosenthal L, De Heer H, Aguirre M, Flores L, Vasquez E, et al. Use of community-based participatory research to disseminate baseline results for building a cardiovascular disease randomized community trial for Mexican Americans living in a US-Mexico border community. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2009;22(3):279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balcázar H, Alvarado M, Cantu F, Pedregon V, Fulwood R. A promotora de salud model for addressing cardiovascular disease risk factors in the US-Mexico border region. Prev Chronic Dis. 2009;6(1):A02. http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2009/jan/08_0020.htm . - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

