VDAC structure, selectivity, and dynamics
- PMID: 22240010
- PMCID: PMC3327780
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.12.026
VDAC structure, selectivity, and dynamics
Abstract
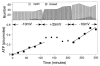
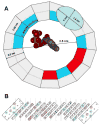
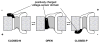
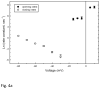
VDAC channels exist in the mitochondrial outer membrane of all eukaryotic organisms. Of the different isoforms present in one organism, it seems that one of these is the canonical VDAC whose properties and 3D structure are highly conserved. The fundamental role of these channels is to control the flux of metabolites between the cytosol and mitochondrial spaces. Based on many functional studies, the fundamental structure of the pore wall consists of one α helix and 13 β strands tilted at a 46° angle. This results in a pore with an estimated internal diameter of 2.5nm. This structure has not yet been resolved. The published 3D structure consists of 19 β strands and is different from the functional structure that forms voltage-gated channels. The selectivity of the channel is exquisite, being able to select for ATP over molecules of the same size and charge. Voltage gating involves two separate gating processes. The mechanism involves the translocation of a positively charged portion of the wall of the channel to the membrane surface resulting in a reduction in pore diameter and volume and an inversion in ion selectivity. This mechanism is consistent with experiments probing changes in selectivity, voltage gating, kinetics and energetics. Other published mechanisms are in conflict with experimental results. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: VDAC structure, function, and regulation of mitochondrial metabolism.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Colombini M. Candidate for the permeability pathway of the outer mitochondrial-membrane. Nature. 1979;279:643–645. - PubMed
-
- Schein SJ, Colombini M, Finkelstein A. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from Paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1976;30:99–120. - PubMed
-
- Colombini M. Voltage gating in the mitochondrial channel, VDAC. J Membr Biol. 1989;111:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Kayser H, Kratzin HD, Thinnes FP, Gotz H, Schmidt WE, Eckart K, Hilschmann N. To the knowledge of human porins. 2. Characterization and primary structure of a 31-kDa porin from human b-lymphocytes (porin 31 HL) Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler. 1989;370:1265–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

