Dual-energy X-ray performs as well as clinical computed tomography for the measurement of visceral fat
- PMID: 22240726
- PMCID: PMC3343346
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2011.367
Dual-energy X-ray performs as well as clinical computed tomography for the measurement of visceral fat
Abstract
Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) is associated with adverse health effects including cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. We developed a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement of visceral adipose tissue (DXA-VAT) as a low cost and low radiation alternative to computed tomography (CT). DXA-VAT was compared to VAT assessed using CT by an expert reader (E-VAT). In addition, the same CT slice was also read by a clinical radiographer (C-VAT) and a best-fit anthropomorphic and demographic VAT model (A-VAT) was developed. Whole body DXA, CT at L4-L5, and anthropometry were measured on 272 black and white South African women (age 29 ± 8 years, BMI 28 ± 7 kg/m(2), waist circumference (WC) 89 ± 16 cm). Approximately one-half of the dataset (n = 141) was randomly selected and used as a training set for the development of DXA-VAT and A-VAT, which were then used to estimate VAT on the remaining 131 women in a blinded fashion. DXA-VAT (r = 0.93, standard error of the estimate (SEE) = 16 cm(2)) and C-VAT (r = 0.93, SEE = 16 cm(2)) were strongly correlated to E-VAT. These correlations with E-VAT were significantly stronger (P < 0.001) than the correlations of individual anthropometry measurements and the A-VAT model (WC + age, r = 0.79, SEE = 27 cm(2)). The inclusion of anthropometric and demographic measurements did not substantially improve the correlation between DXA-VAT and E-VAT. DXA-VAT performed as well as a clinical read of VAT from a CT scan and better than anthropomorphic and demographic models.
Figures
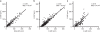
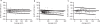
References
-
- Bouchard C. BMI, fat mass, abdominal adiposity and visceral fat: where is the 'beef'. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007;31:1552–1553. - PubMed
-
- Schoeller DA, Tylavsky FA, Baer DJ.et al. QDR 4500A dual-energy X-ray absorptiometer underestimates fat mass in comparison with criterion methods in adults Am J Clin Nutr 2005811018–1025. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Wang Z, Lohman T.et al. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is a valid tool for assessing skeletal muscle mass in older women J Nutr 20071372775–2780. - PubMed
-
- Blake GM, Naeem M, Boutros M. Comparison of effective dose to children and adults from dual X-ray absorptiometry examinations. Bone. 2006;38:935–942. - PubMed
-
- Lee K, Lee S, Kim YJ, Kim YJ. Waist circumference, dual-energy X-ray absortiometrically measured abdominal adiposity, and computed tomographically derived intra-abdominal fat area on detecting metabolic risk factors in obese women. Nutrition. 2008;24:625–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

