Kidney dysfunction and cognitive decline in women
- PMID: 22241818
- PMCID: PMC3302680
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05330611
Kidney dysfunction and cognitive decline in women
Abstract
Background and objectives: ESRD is associated with substantial cognitive deficits but whether earlier kidney dysfunction predicts cognitive decline is less well defined.
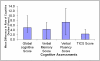
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: More than 1700 women aged ≥70 years in the Nurses' Health Study had plasma creatinine and urinary albumin/creatinine ratios (ACRs) measured in 2000, within 12 months of their initial cognitive testing. These participants had repeated assessments of cognition administered by phone every 2 years, including tests for general cognition, verbal memory, verbal fluency, and working memory for up to 6 years of follow-up. Mixed-effects regression analysis was applied to calculate mean differences in the rate of cognitive decline between women with an estimated GFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) or an ACR ≥5 mg/g versus referent levels.
Results: The median age was 74 years at initial cognitive testing, 99% of women were Caucasian, median plasma creatinine was 0.8 mg/dl, and 25% had an ACR ≥5 mg/g. The difference in cognitive decline with a baseline ACR ≥5 mg/g versus an ACR <5 mg/g was equivalent to the difference observed with 2-7 years of aging; that is, a higher ACR was associated with 2-7 times faster decline in all four cognitive domains assessed (all P values <0.05) than that attributed to each 1 year of aging alone. No associations were observed between an eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) and cognitive decline.
Conclusions: A baseline urinary ACR ≥5 mg/g, a level not traditionally considered clinically significant, is independently associated with faster decline in cognitive function.
Figures
Comment in
-
Albuminuria and cognitive impairment.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Mar;7(3):376-8. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00210112. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22282483 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stevens LA, Li S, Wang C, Huang C, Becker BN, Bomback AS, Brown WW, Burrows NR, Jurkovitz CT, McFarlane SI, Norris KC, Shlipak M, Whaley-Connell AT, Chen S-C, Bakris GL, McCullough PA: Prevalence of CKD and comorbid illness in elderly patients in the United States: Results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP). Am J Kidney Dis 55[Suppl 2]: S23–S33, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Griva K, Stygall J, Hankins M, Davenport A, Harrison M, Newman SP: Cognitive impairment and 7-year mortality in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 56: 693–703, 2010 - PubMed
-
- McClellan WM, Langston RD, Presley R: Medicare patients with cardiovascular disease have a high prevalence of chronic kidney disease and a high rate of progression to end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1912–1919, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Hallé JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf S; HOPE Study Investigators: Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA 286: 421–426, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous