The effect of hyoscine butylbromide in shortening the first stage of labor: A double blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial
- PMID: 22241946
- PMCID: PMC3253756
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S16415
The effect of hyoscine butylbromide in shortening the first stage of labor: A double blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hyoscine butylbromide (HBB) is widely used in labor rooms. There have been many studies on the use of HBB during labor with conflicting results, involving both primiparous and multiparous women. The aim of this trial was to study the efficacy of HBB for shortening the first stage of labor in primiparous women.
Methods: The study was a randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Ninety-seven primigravid term pregnant women in spontaneous labor received either hyoscine butylbromide or a placebo intramuscularly once the women entered the active phase of labor. The primary outcome measured was the duration of the first stage of labor. Secondary outcomes were the duration of the second and third stages of labor, blood loss at delivery, rate of cesarean section, and Apgar scores for the neonates.
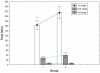
Results: A total of 97 women yielded data for analysis. Of these, 45 women received the placebo and 52 received HBB. The mean duration of the first stage in the control group was 215 minutes, compared with 165 minutes in the study group, representing a decrease of 23.3% (P = 0.001). There were no significant changes in the duration of the second (P = 0.063) or third (P = 0.0418) stages of labor, and no significant differences in blood loss or Apgar scores. There was a slightly higher (but statistically insignificant) rate of instrumental delivery in the control group, but no difference in the Cesarean section rate. There was a 60% reduction in opioid analgesic use in the HBB group.
Conclusion: HBB is effective in significantly reducing the duration of the first stage of labor, and is not associated with any apparent adverse maternal or neonatal outcomes.
Keywords: augmentation; duration; first stage; hyoscine butylbromide; labor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of hyoscine n- butylbromide on labor progress: A systematic review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 May 13;20(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-2832-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32404072 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intravenous hyoscine-N-butyl bromide on active phase of labor progress: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015 Jun;28(9):1038-42. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.942628. Epub 2014 Jul 30. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015. PMID: 25023433 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of hyoscine butylbromide on the first stage of labour in term pregnancies.BJOG. 2007 Dec;114(12):1542-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01497.x. Epub 2007 Sep 27. BJOG. 2007. PMID: 17903230 Clinical Trial.
-
Does hyoscine N-butylbromide shorten the active phase in labor? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020 Dec;46(12):2629-2644. doi: 10.1111/jog.14507. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020. PMID: 33029904
-
Efficacy of hyoscine butyl-bromide in shortening the active phase of labor: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020 Sep;252:218-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.06.042. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020. PMID: 32629224
Cited by
-
The effect of hyoscine n- butylbromide on labor progress: A systematic review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 May 13;20(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-2832-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32404072 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review automation technologies.Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 9;3:74. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-3-74. Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25005128 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of intravenous hyoscine butylbromide on slow progress in labor (BUSCLAB): A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2024 Mar 28;21(3):e1004352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004352. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Med. 2024. PMID: 38547322 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Effects of Hyoscine Butylbromide in Childhood.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 26;14(9):3009. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093009. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immediate dilation of a tight or stenotic cervix by intra-procedural administration of hyoscine butylbromide: A clinical trial.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2019 May 28;17(4):253-60. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v17i4.4550. eCollection 2019 Apr. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31435605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez-Zeno JA, Peaceman AM, Adashek JA, Socol ML. A controlled trial of a program for the active management of labour. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:450–454. - PubMed
-
- Frigoletto FD, Jr, Lieberman E, Lang JM, et al. A clinical trial of active management of labour. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:745–750. - PubMed
-
- Sadler LC, Davison T, McCowan LM. A randomised controlled trial and meta-analysis of active management of labour. BJOG. 2000;107(7):909–915. - PubMed
-
- Hotwani J, Ainapure SS. Hyoscine butylbromide suppositories. Indian Medical Gaz. 2000:217–219.
-
- Corsen G. A study of the use and mode of action of the antispasmodic drug Buscopan in gynecology and obstetrics. Med Klin. 1983;48:2186–2188.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

