Requirement of nuclear factor κB for Smac mimetic-mediated sensitization of pancreatic carcinoma cells for gemcitabine-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 22241962
- PMCID: PMC3257191
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.11460
Requirement of nuclear factor κB for Smac mimetic-mediated sensitization of pancreatic carcinoma cells for gemcitabine-induced apoptosis
Abstract
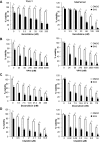
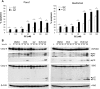
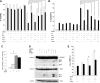
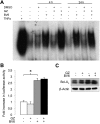
Defects in apoptosis contribute to treatment resistance and poor outcome of pancreatic cancer, calling for novel therapeutic strategies. Here, we provide the first evidence that nuclear factor (NF) κB is required for Smac mimetic-mediated sensitization of pancreatic carcinoma cells for gemcitabine-induced apoptosis. The Smac mimetic BV6 cooperates with gemcitabine to reduce cell viability and to induce apoptosis. In addition, BV6 significantly enhances the cytotoxicity of several anticancer drugs against pancreatic carcinoma cells, including doxorubicin, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil. Molecular studies reveal that BV6 stimulates NF-κB activation, which is further increased in the presence of gemcitabine. Importantly, inhibition of NF-κB by overexpression of the dominant-negative IκBα superrepressor significantly decreases BV6- and gemcitabine-induced apoptosis, demonstrating that NF-κB exerts a proapoptotic function in this model of apoptosis. In support of this notion, inhibition of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) by the TNFα blocking antibody Enbrel reduces BV6- and gemcitabine-induced activation of caspase 8 and 3, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and apoptosis. By demonstrating that BV6 and gemcitabine trigger a NF-κB-dependent, TNFα-mediated loop to activate apoptosis signaling pathways and caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death, our findings have important implications for the development of Smac mimetic-based combination protocols in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of non-canonical NF-κB signaling as a critical mediator of Smac mimetic-stimulated migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Mar 28;4(3):e564. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.70. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23538445 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB is required for Smac mimetic-mediated sensitization of glioblastoma cells for γ-irradiation-induced apoptosis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Oct;10(10):1867-75. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0218. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21859841
-
Smac mimetic triggers necroptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells when caspase activation is blocked.Cancer Lett. 2016 Sep 28;380(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.05.036. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27267809
-
Smac mimetic sensitizes glioblastoma cells to Temozolomide-induced apoptosis in a RIP1- and NF-κB-dependent manner.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 21;32(8):988-97. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.108. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22469979
-
Smac mimetics and TNFalpha: a dangerous liaison?Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):655-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.042. Cell. 2007. PMID: 18022360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Key necroptotic proteins are required for Smac mimetic-mediated sensitization of cholangiocarcinoma cells to TNF-α and chemotherapeutic gemcitabine-induced necroptosis.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 8;15(1):e0227454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227454. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31914150 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer subclonal genetic architecture as a key to personalized medicine.Neoplasia. 2013 Dec;15(12):1410-20. doi: 10.1593/neo.131972. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 24403863 Free PMC article.
-
The SMAC mimetic BV6 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to ionizing radiation by interfering with DNA repair processes and enhancing apoptosis.Radiat Oncol. 2015 Sep 17;10:198. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0507-4. Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26383618 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-targeting peptides@PMO, a mimetic to the pro-apoptotic protein Smac/DIABLO for selective activation of apoptosis in cancer cells.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 29;14:1237478. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1237478. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37711175 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of DR5 as a critical, NF-κB-regulated mediator of Smac-induced apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Nov 28;4(11):e936. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.457. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24287697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363:1049–1057. - PubMed
-
- Fulda S, Debatin KM. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene. 2006;25:4798–4811. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:99–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
