Short conduction delays cause inhibition rather than excitation to favor synchrony in hybrid neuronal networks of the entorhinal cortex
- PMID: 22241969
- PMCID: PMC3252263
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002306
Short conduction delays cause inhibition rather than excitation to favor synchrony in hybrid neuronal networks of the entorhinal cortex
Abstract
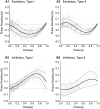
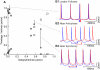
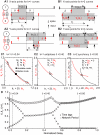
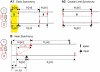
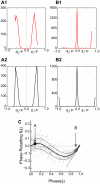
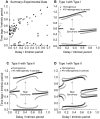
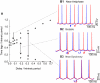
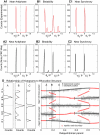
How stable synchrony in neuronal networks is sustained in the presence of conduction delays is an open question. The Dynamic Clamp was used to measure phase resetting curves (PRCs) for entorhinal cortical cells, and then to construct networks of two such neurons. PRCs were in general Type I (all advances or all delays) or weakly type II with a small region at early phases with the opposite type of resetting. We used previously developed theoretical methods based on PRCs under the assumption of pulsatile coupling to predict the delays that synchronize these hybrid circuits. For excitatory coupling, synchrony was predicted and observed only with no delay and for delays greater than half a network period that cause each neuron to receive an input late in its firing cycle and almost immediately fire an action potential. Synchronization for these long delays was surprisingly tight and robust to the noise and heterogeneity inherent in a biological system. In contrast to excitatory coupling, inhibitory coupling led to antiphase for no delay, very short delays and delays close to a network period, but to near-synchrony for a wide range of relatively short delays. PRC-based methods show that conduction delays can stabilize synchrony in several ways, including neutralizing a discontinuity introduced by strong inhibition, favoring synchrony in the case of noisy bistability, and avoiding an initial destabilizing region of a weakly type II PRC. PRCs can identify optimal conduction delays favoring synchronization at a given frequency, and also predict robustness to noise and heterogeneity.
© 2012 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bland BH, Colom LV. Extrinsic and intrinsic properties underlying oscillation and synchrony in limbic cortex. Prog Neurobiol. 1993;41:157–208. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron. 2002;33:325–340. - PubMed
-
- Squire LR, Zola-Morgan S. The medial temporal lobe memory system. Science. 1991;253:1380–1386. - PubMed
-
- Stewart M, Fox SE. Do septal neurons pace the hippocampal theta rhythm? Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:163–168. - PubMed
-
- Singer W. Synchronization of cortical activity and its putative role in information processing and learning. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:349–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

