The Caenorhabditis elegans synthetic multivulva genes prevent ras pathway activation by tightly repressing global ectopic expression of lin-3 EGF
- PMID: 22242000
- PMCID: PMC3248470
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002418
The Caenorhabditis elegans synthetic multivulva genes prevent ras pathway activation by tightly repressing global ectopic expression of lin-3 EGF
Abstract
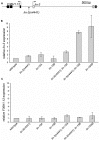
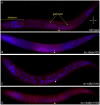
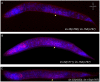
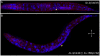
The Caenorhabditis elegans class A and B synthetic multivulva (synMuv) genes redundantly antagonize an EGF/Ras pathway to prevent ectopic vulval induction. We identify a class A synMuv mutation in the promoter of the lin-3 EGF gene, establishing that lin-3 is the key biological target of the class A synMuv genes in vulval development and that the repressive activities of the class A and B synMuv pathways are integrated at the level of lin-3 expression. Using FISH with single mRNA molecule resolution, we find that lin-3 EGF expression is tightly restricted to only a few tissues in wild-type animals, including the germline. In synMuv double mutants, lin-3 EGF is ectopically expressed at low levels throughout the animal. Our findings reveal that the widespread ectopic expression of a growth factor mRNA at concentrations much lower than that in the normal domain of expression can abnormally activate the Ras pathway and alter cell fates. These results suggest hypotheses for the mechanistic basis of the functional redundancy between the tumor-suppressor-like class A and B synMuv genes: the class A synMuv genes either directly or indirectly specifically repress ectopic lin-3 expression; while the class B synMuv genes might function similarly, but alternatively might act to repress lin-3 as a consequence of their role in preventing cells from adopting a germline-like fate. Analogous genes in mammals might function as tumor suppressors by preventing broad ectopic expression of EGF-like ligands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Normanno N, De Luca A, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene. 2006;366:2–16. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. Transforming growth factor-alpha. A model for membrane-anchored growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:21393–21396. - PubMed
-
- Yotsumoto F, Yagi H, Suzuki SO, Oki E, Tsujioka H, et al. Validation of HB-EGF and amphiregulin as targets for human cancer therapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;365:555–561. - PubMed
-
- Jhappan C, Stahle C, Harkins RN, Fausto N, Smith GH, et al. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990;61:1137–1146. - PubMed
-
- Sandgren EP, Luetteke NC, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL, Lee DC. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990;61:1121–1135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

