Autosomal recessive dilated cardiomyopathy due to DOLK mutations results from abnormal dystroglycan O-mannosylation
- PMID: 22242004
- PMCID: PMC3248466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002427
Autosomal recessive dilated cardiomyopathy due to DOLK mutations results from abnormal dystroglycan O-mannosylation
Abstract
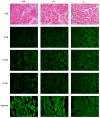
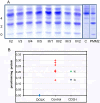
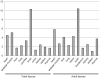
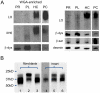
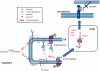
Genetic causes for autosomal recessive forms of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) are only rarely identified, although they are thought to contribute considerably to sudden cardiac death and heart failure, especially in young children. Here, we describe 11 young patients (5-13 years) with a predominant presentation of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Metabolic investigations showed deficient protein N-glycosylation, leading to a diagnosis of Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDG). Homozygosity mapping in the consanguineous families showed a locus with two known genes in the N-glycosylation pathway. In all individuals, pathogenic mutations were identified in DOLK, encoding the dolichol kinase responsible for formation of dolichol-phosphate. Enzyme analysis in patients' fibroblasts confirmed a dolichol kinase deficiency in all families. In comparison with the generally multisystem presentation in CDG, the nonsyndromic DCM in several individuals was remarkable. Investigation of other dolichol-phosphate dependent glycosylation pathways in biopsied heart tissue indicated reduced O-mannosylation of alpha-dystroglycan with concomitant functional loss of its laminin-binding capacity, which has been linked to DCM. We thus identified a combined deficiency of protein N-glycosylation and alpha-dystroglycan O-mannosylation in patients with nonsyndromic DCM due to autosomal recessive DOLK mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
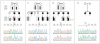

References
-
- Michels VV, Moll PP, Miller FA, Tajik AJ, Chu JS, et al. The frequency of familial dilated cardiomyopathy in a series of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Grunig E, Tasman JA, Kucherer H, Franz W, Kubler W, et al. Frequency and phenotypes of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Baig MK, Goldman JH, Caforio AL, Coonar AS, Keeling PJ, et al. Familial dilated cardiomyopathy: cardiac abnormalities are common in asymptomatic relatives and may represent early disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Sinagra G, Di Lenarda A, Brodsky GL, Taylor MR, Muntoni F, et al. Current perspective new insights into the molecular basis of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Ital Heart J. 2001;2:280–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

