Polycystic diseases in visceral organs
- PMID: 22242024
- PMCID: PMC3253486
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/609370
Polycystic diseases in visceral organs
Abstract
Primary cilia are nonmotile, microtubule-based, antenna-like organelles projecting from the apical surface of most mammalian cells. Elegant studies have established the importance of ciliary structure and function in signal transduction and the sensory roles of cilia in maintaining healthy cellular state. In particular, dysfunctional cilia have been implicated in a large number of diseases mainly characterized by the presence of fluid-filled cysts in various organs. Aside from polycystic kidney disease (PKD), however, the roles of cilia in polycystic liver disease (PLD), polycystic pancreas disease (PPD), and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) are still very vague. In addition, although gender and sex hormones are known to regulate cyst formation, their roles in regulating physiological functions of cilia need to be further explored.
Figures
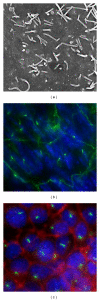
References
-
- Christensen ST, Pedersen SF, Satir P, Veland IR, Schneider L. The primary cilium coordinates signaling pathways in cell cycle control and migration during development and tissue repair. Current Topics in Developmental Biology. 2008;85:261–301. - PubMed
-
- Nauli SM, Haymour HS, AbouAlaiwi WA, Lo ST, Nauli AM. Mechanosensitivity and Mechanotransduction. chapter 14. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2001. Primary cilia are mechanosensory organelles in vestibular tissues.
-
- Singla V, Reiter JF. The primary cilium as the cell’s antenna: signaling at a sensory organelle. Science. 2006;313(5787):629–633. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

