The project HICARE: cross-sectoral action alliance against multi-resistant pathogens
- PMID: 22242106
- PMCID: PMC3252650
- DOI: 10.3205/dgkh000182
The project HICARE: cross-sectoral action alliance against multi-resistant pathogens
Abstract
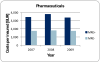
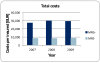
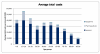
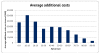
Multi-resistant pathogens are a serious problem on a considerable scale for the health sector. Patients with infections induced by multi-resistant bacteria cause enormous additional treatment costs of around 20,500 € per insured. Due to the recently used billing and documentation system there is a significant shortage of information transparency. The guidelines for hospital hygiene and infection prevention published by the Robert Koch Institute (RKI) include a presumption provision, which means that subject to compliance with these guidelines the observance of the current state of medical science is suspected. In case of a derogation, a scientific justification is necessary, which is used e.g. in connection with liability questions. Within the framework of legal reforms in 2011, the legislator aspires a nationwide improvement of hygiene quality in medical institutions and information transparency. Many specific issues about the general reporting obligation of infections with multi-resistant pathogens or about the standardized exchange of infection documentations between medical institution and health authority remain unresolved.Regional, cross-sectoral networks create the base to tackle targeted measures collectively and may develop sustainable and tailored solutions for their region. With these considerations in mind, the project HICARE was founded in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The project pursues the aim to develop an intervention strategy against the spread of multi-resistant pathogens. Health insurances make an important contribution to quality of medical treatment by participation.
Multiresistente Erreger (MRE) stellen ein ernstzunehmendes Problem erheblichen Ausmaßes für den Gesundheitssektor dar. Patienten mit MRE induzierten Infektionen verursachen immense zusätzliche Behandlungskosten von rund 20.500 € pro Versichertem. Aufgrund des derzeit genutzten pauschalen Abrechnungs- bzw. Dokumentationssystems besteht ein erheblicher Mangel an Informationstransparenz. Die vom Robert Koch-Institut (RKI) veröffentlichen Empfehlungen zur Krankenhaushygiene und Infektionsprävention beinhalten eine sog. Vermutungsregelung, d.h. bei ihrer Einhaltung wird vermutet, dass der Stand der medizinischen Wissenschaft beachtet worden ist. Im Fall der Abweichung muss dafür eine wissenschaftliche Begründung gegeben werden, was z.B. bei Haftungsfragen zugrunde gelegt wird. Im Rahmen gesetzlicher Neuerungen strebt der Gesetzgeber 2011 eine bundesweite Verbesserung der Hygienequalität in medizinischen Einrichtungen sowie der Informationstransparenz an. Viele konkrete Fragen über die allgemeine Meldepflicht für Infektionen mit MRE oder über den standardisierten Austausch von Infektionsdokumentationen zwischen medizinischer Einrichtung und Gesundheitsbehörde bleiben jedoch weiterhin offen.
Regionale, sektorübergreifende Netzwerke schaffen die Basis, Maßnahmen gezielt im Team anzugehen und können auf diese Weise nachhaltige, für ihre Region zugeschnittene Lösungen entwickeln. Unter diesen Gesichtspunkten bildete sich auch das Projekt HICARE in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern heraus. Das Projekt verfolgt das Ziel, Interventionsstrategien gegen die Ausbreitung von MRE zu entwickeln. Krankenkassen leisten durch ihre Mitwirkung einen wichtigen Beitrag zur Versorgungsqualität.
Keywords: Law of Infection Protection; Staphylococcus aureus; cost analysis; health insurance; infection documentation; project HICARE.
Figures

References
-
- Gastmeier P, Geffers C. Nosokomiale Infektionen in Deutschland: Wie viele gibt es wirklich? Eine Schätzung für das Jahr 2006. Dtsch med Wochenschr. 2008;133(21):1111–1115. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1077224. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1077224. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Linder R, Horenkamp-Sonntag D, Pfenning I, Verheyen F. Quantifizierung stationärer Patientenfallzahlen mit nicht-dokumentierter Infektion multiresistenter Erreger. AGENS Methoden Workshop; Köln, 14.-15.04.2011; Hamburg: Wissenschaftliches Institut der TK für Nutzen und Effizienz im Gesundheitswesen; 2011. Available from: http://www.tk.de/centaurus/servlet/contentblob/339556/Datei/6664/Nicht-D....
-
- Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung. Bevölkerungsgruppen nach Altersgruppen und Geschlecht. Altersgruppen in absoluten Zahlen, Anteile der Geschlechter in Prozent. 2009.
-
- Friedrich AW. EUREGIO MRSA-net Twente/Münsterland: „search & follow“ by Euregional network building. Gesundheitswesen. 2009;71(11):766–770. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1241892. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1241892. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lohmann H. Visionen brauchen Fantasie. Stuttgart: Thieme; 2009.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

