Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers for early stage breast cancer detection
- PMID: 22242178
- PMCID: PMC3252341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029770
Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers for early stage breast cancer detection
Abstract
Introduction: MicroRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) are a class of small, non-coding RNA molecules with relevance as regulators of gene expression thereby affecting crucial processes in cancer development. MiRNAs offer great potential as biomarkers for cancer detection due to their remarkable stability in blood and their characteristic expression in many different diseases. We investigated whether microarray-based miRNA profiling on whole blood could discriminate between early stage breast cancer patients and healthy controls.
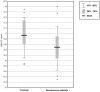
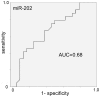
Methods: We performed microarray-based miRNA profiling on whole blood of 48 early stage breast cancer patients at diagnosis along with 57 healthy individuals as controls. This was followed by a real-time semi-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) validation in a separate cohort of 24 early stage breast cancer patients from a breast cancer screening unit and 24 age matched controls using two differentially expressed miRNAs (miR-202, miR-718).
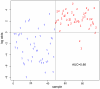
Results: Using the significance level of p<0.05, we found that 59 miRNAs were differentially expressed in whole blood of early stage breast cancer patients compared to healthy controls. 13 significantly up-regulated miRNAs and 46 significantly down-regulated miRNAs in our microarray panel of 1100 miRNAs and miRNA star sequences could be detected. A set of 240 miRNAs that was evaluated by radial basis function kernel support vector machines and 10-fold cross validation yielded a specificity of 78.8%, and a sensitivity of 92.5%, as well as an accuracy of 85.6%. Two miRNAs were validated by RT-qPCR in an independent cohort. The relative fold changes of the RT-qPCR validation were in line with the microarray data for both miRNAs, and statistically significant differences in miRNA-expression were found for miR-202.
Conclusions: MiRNA profiling in whole blood has potential as a novel method for early stage breast cancer detection, but there are still challenges that need to be addressed to establish these new biomarkers in clinical use.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell. 2001;107:823–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

