General molecular biology and architecture of nuclear receptors
- PMID: 22242852
- PMCID: PMC3637177
- DOI: 10.2174/156802612799436641
General molecular biology and architecture of nuclear receptors
Abstract
Nuclear receptors (NRs) regulate and coordinate multiple processes by integrating internal and external signals, thereby maintaining homeostasis in front of nutritional, behavioral and environmental challenges. NRs exhibit strong similarities in their structure and mode of action: by selective transcriptional activation or repression of cognate target genes, which can either be controlled through a direct, DNA binding-dependent mechanism or through crosstalk with other transcriptional regulators, NRs modulate the expression of gene clusters thus achieving coordinated tissue responses. Additionally, non genomic effects of NR ligands appear mediated by ill-defined mechanisms at the plasma membrane. These effects mediate potential therapeutic effects as small lipophilic molecule targets, and many efforts have been put in elucidating their precise mechanism of action and pathophysiological roles. Currently, numerous nuclear receptor ligand analogs are used in therapy or are tested in clinical trials against various diseases such as hypertriglyceridemia, atherosclerosis, diabetes, allergies and cancer and others.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

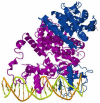

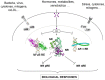
References
-
- Escriva GH, Laudet V, Robinson-Rechavi M. Nuclear receptors are markers of animal genome evolution. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2003;3:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger C, Hollenberg SM, Rosenfeld MG, Evans RM. Domain structure of human glucocorticoid receptor and its relationship to the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1985;318:670–672. - PubMed
-
- Greene GL, Gilna P, Waterfield M, Baker A, Hort Y, Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986;231:1150–1154. - PubMed

