Inducible alkylation of DNA by a quinone methide-peptide nucleic acid conjugate
- PMID: 22243337
- PMCID: PMC3277674
- DOI: 10.1021/bi201492b
Inducible alkylation of DNA by a quinone methide-peptide nucleic acid conjugate
Abstract
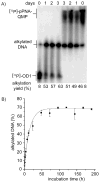
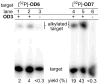
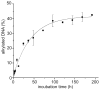
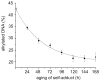
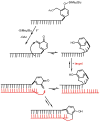
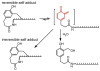
The reversibility of alkylation by a quinone methide intermediate (QM) avoids the irreversible consumption that plagues most reagents based on covalent chemistry and allows for site specific reaction that is controlled by the thermodynamics rather than kinetics of target association. This characteristic was originally examined with an oligonucleotide QM conjugate, but broad application depends on alternative derivatives that are compatible with a cellular environment. Now, a peptide nucleic acid (PNA) derivative has been constructed and shown to exhibit an equivalent ability to delivery the reactive QM in a controlled manner. This new conjugate demonstrates high selectivity for a complementary sequence of DNA even when challenged with an alternative sequence containing a single T/T mismatch. Alternatively, alkylation of noncomplementary sequences is only possible when a template strand is present to colocalize the conjugate and its target. For efficient alkylation in this example, a single-stranded region of the target is required adjacent to the QM conjugate. Most importantly, the intrastrand self-adducts formed between the PNA and its attached QM remained active and reversible over more than 8 days in aqueous solution prior to reaction with a chosen target added subsequently.
Figures

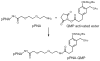

References
-
- Kean JM, Miller PS. Effect of target structure on cross-linking by psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1994;33:9178–9186. - PubMed
-
- Kim KH, Nielsen PE, Glazer PM. Site-specific gene modification by PNAs conjugate to psoralen. Biochemistry. 2006;45:314–323. - PubMed
-
- Warpehoski MA, Hurley LH. Sequence selectivity of DNA covalent modification. Chem Res Toxicol. 1988;1:315–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

