Integrated vector management for malaria control in Uganda: knowledge, perceptions and policy development
- PMID: 22243516
- PMCID: PMC3280926
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-21
Integrated vector management for malaria control in Uganda: knowledge, perceptions and policy development
Abstract
Background: Integrated vector management (IVM) is increasingly being recommended as an option for sustainable malaria control. However, many malaria-endemic countries lack a policy framework to guide and promote the approach. The objective of the study was to assess knowledge and perceptions in relation to current malaria vector control policy and IVM in Uganda, and to make recommendations for consideration during future development of a specific IVM policy.
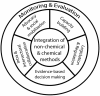
Methods: The study used a structured questionnaire to interview 34 individuals working at technical or policy-making levels in health, environment, agriculture and fisheries sectors. Specific questions on IVM focused on the following key elements of the approach: integration of chemical and non-chemical interventions of vector control; evidence-based decision making; inter-sectoral collaboration; capacity building; legislation; advocacy and community mobilization.
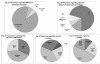
Results: All participants were familiar with the term IVM and knew various conventional malaria vector control (MVC) methods. Only 75% thought that Uganda had a MVC policy. Eighty percent (80%) felt there was inter-sectoral collaboration towards IVM, but that it was poor due to financial constraints, difficulties in involving all possible sectors and political differences. The health, environment and agricultural sectors were cited as key areas requiring cooperation in order for IVM to succeed. Sixty-seven percent (67%) of participants responded that communities were actively being involved in MVC, while 48% felt that the use of research results for evidence-based decision making was inadequate or poor. A majority of the participants felt that malaria research in Uganda was rarely used to facilitate policy changes. Suggestions by participants for formulation of specific and effective IVM policy included: revising the MVC policy and IVM-related policies in other sectors into a single, unified IVM policy and, using legislation to enforce IVM in development projects.
Conclusion: Integrated management of malaria vectors in Uganda remains an underdeveloped component of malaria control policy. Cooperation between the health and other sectors needs strengthening and funding for MVC increased in order to develop and effectively implement an appropriate IVM policy. Continuous engagement of communities by government as well as monitoring and evaluation of vector control programmes will be crucial for sustaining IVM in the country.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consolidating tactical planning and implementation frameworks for integrated vector management in Uganda.Malar J. 2016 Apr 14;15:214. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1269-7. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 27074809 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated vector management for malaria control.Malar J. 2008 Dec 11;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-7-S1-S4. Malar J. 2008. PMID: 19091038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strengthening community and stakeholder participation in the implementation of integrated vector management for malaria control in western Kenya: a case study.Malar J. 2021 Mar 19;20(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03692-4. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33740983 Free PMC article.
-
Getting ready for integrated vector management for improved disease prevention in Zimbabwe: a focus on key policy issues to consider.Malar J. 2019 Sep 23;18(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2965-x. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31547828 Free PMC article.
-
Current vector control challenges in the fight against malaria.Acta Trop. 2017 Oct;174:91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.06.028. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 28684267 Review.
Cited by
-
An Assessment of Participatory Integrated Vector Management for Malaria Control in Kenya.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Nov;123(11):1145-51. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408748. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25859686 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of Information in Decision-Analytic Modeling for Malaria Vector Control in East Africa.Risk Anal. 2017 Feb;37(2):231-244. doi: 10.1111/risa.12606. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Risk Anal. 2017. PMID: 27008340 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable malaria control: transdisciplinary approaches for translational applications.Malar J. 2012 Dec 26;11:431. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-431. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 23268712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examining the impact of larval source management and insecticide-treated nets using a spatial agent-based model of Anopheles gambiae and a landscape generator tool.Malar J. 2013 Aug 21;12:290. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-290. Malar J. 2013. PMID: 23965136 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of fifth serotype of dengue virus (DENV-5): A new public health dilemma in dengue control.Med J Armed Forces India. 2015 Jan;71(1):67-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Med J Armed Forces India. 2015. PMID: 25609867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. Malaria vector control and personal protection: report of a WHO study group. WHO technical report series 936. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2006. - PubMed
-
- WHO. A global strategy for malaria control. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1993.
-
- RBM. Key facts, figures and strategies: the Global Malaria Action Plan. Roll Back Malaria Partnership; 2008.
-
- Lengeler C. Insecticide-treated bed nets and curtains for preventing malaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2:CD000363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

