Pancreatic head resection and Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy for the treatment of the focal form of congenital hyperinsulinism
- PMID: 22244405
- PMCID: PMC3595012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.10.032
Pancreatic head resection and Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy for the treatment of the focal form of congenital hyperinsulinism
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the outcome of patients who underwent pancreatic head resection and Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy to the remaining normal pancreatic body and tail for the treatment of a focal lesion in the pancreatic head causing congenital hyperinsulinism (HI).
Methods: One hundred thirty-eight patients underwent pancreatic resection for focal HI between 1998 and 2010. Twenty-three patients in the group underwent pancreatic head resection and Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy.
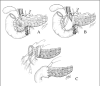
Results: There were 13 females and 10 males. Median age and weight at surgery were 8 weeks and 5.8 kg, respectively. Twenty-one patients had a near-total pancreatic head resection, and 2 patients had a pylorus-preserving Whipple procedure. The pancreaticojejunostomy anastomosis was performed with interrupted fine monofilament sutures such that the transected end of the pancreatic body was tucked within the end of the Roux-en-Y jejunal limb. Median hospital stay was 22 days. All patients were cured of HI.
Conclusion: We conclude that pancreatic head resection with Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy is a safe and effective procedure for the treatment of the HI patient with a large focal lesion in the pancreatic head that is not amenable to local resection alone.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pancreatic head resection preserving the main pancreatic duct for congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy.Pediatr Surg Int. 2012 Sep;28(9):935-7. doi: 10.1007/s00383-012-3147-x. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012. PMID: 22885732
-
Indications and outcomes of duodenum-preserving resection of the pancreatic head in children.Pediatr Surg Int. 2019 Apr;35(4):449-455. doi: 10.1007/s00383-018-4410-6. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Pediatr Surg Int. 2019. PMID: 30386905
-
A multidisciplinary approach to the focal form of congenital hyperinsulinism leads to successful treatment by partial pancreatectomy.J Pediatr Surg. 2004 Mar;39(3):270-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2003.11.019. J Pediatr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15017536
-
Local resection of the head of the pancreas with pancreaticojejunostomy.J Gastrointest Surg. 2005 Jul-Aug;9(6):863-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.09.029. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005. PMID: 16189887 Review. No abstract available.
-
[New aspects of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Principles, results and evidence].Pathologe. 2012 Nov;33 Suppl 2:258-65. doi: 10.1007/s00292-012-1639-z. Pathologe. 2012. PMID: 23108784 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The surgical management of insulinomas in children.J Pediatr Surg. 2013 Dec;48(12):2517-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.04.022. J Pediatr Surg. 2013. PMID: 24314196 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical practice guidelines for congenital hyperinsulinism.Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017;26(3):127-152. doi: 10.1297/cpe.26.127. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28804205 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative Ultrasound: A Tool to Support Tissue-Sparing Curative Pancreatic Resection in Focal Congenital Hyperinsulinism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 22;9:478. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00478. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30186238 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic head resection preserving the main pancreatic duct for congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy.Pediatr Surg Int. 2012 Sep;28(9):935-7. doi: 10.1007/s00383-012-3147-x. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012. PMID: 22885732
-
Congenital hyperinsulinism treated by surgical resection of the hyperplastic lesion which had been preoperatively diagnosed by 18F-DOPA PET examination in Japan: a nationwide survey.Pediatr Surg Int. 2018 Oct;34(10):1093-1098. doi: 10.1007/s00383-018-4315-4. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Pediatr Surg Int. 2018. PMID: 30076450
References
-
- Stanley CA. Hyperinsulinism in infants and children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1997;44:363–74. - PubMed
-
- Arnoux JB, de Lonlay P, Ribeiro MJ, et al. Congenital hyperinsulinism. Early Hum Dev. 2010 May;86:287–94. - PubMed
-
- De León DD, Stanley CA. Mechanisms of disease: advances in diagnosis and treatment of hyperinsulinism in neonates. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:57–68. - PubMed
-
- Brunelle F, Negre V, Barth MO, et al. Pancreatic venous samplings in infants and children with primary hyperinsulinism. Pediatr Radiol. 1989;19:100–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

