O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in glioma therapy: promise and problems
- PMID: 22244911
- PMCID: PMC3340514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.12.004
O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in glioma therapy: promise and problems
Abstract
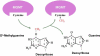
Gliomas are the most frequent adult primary brain tumor, and are invariably fatal. The most common diagnosis glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) afflicts 12,500 new patients in the U.S. annually, and has a median survival of approximately one year when treated with the current standard of care. Alkylating agents have long been central in the chemotherapy of GBM and other gliomas. The DNA repair protein O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), the principal human activity that removes cytotoxic O(6)-alkylguanine adducts from DNA, promotes resistance to anti-glioma alkylators, including temozolomide and BCNU, in GBM cell lines and xenografts. Moreover, MGMT expression assessed by immunohistochemistry, biochemical activity or promoter CpG methylation status is associated with the response of GBM to alkylator-based therapies, providing evidence that MGMT promotes clinical resistance to alkylating agents. These observations suggest a role for MGMT in directing adjuvant therapy of GBM and other gliomas. Promoter methylation status is the most clinically tractable measure of MGMT, and there is considerable enthusiasm for exploring its utility as a marker to assign therapy to individual patients. Here, we provide an overview of the biochemical, genetic and biological characteristics of MGMT as they relate to glioma therapy. We consider current methods to assess MGMT expression and discuss their utility as predictors of treatment response. Particular emphasis is given to promoter methylation status and the methodological and conceptual impediments that limit its use to direct treatment. We conclude by considering approaches that may improve the utility of MGMT methylation status in planning optimal therapies tailored to individual patients.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CpG island hypermethylation of the DNA repair enzyme methyltransferase predicts response to temozolomide in primary gliomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;10(15):4933-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0392. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15297393
-
O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase as a promising target for the treatment of temozolomide-resistant gliomas.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 24;4(10):e876. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.388. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24157870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents.N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 9;343(19):1350-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011093431901. N Engl J Med. 2000. PMID: 11070098
-
dCas9/CRISPR-based methylation of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in malignant glioma.J Neurooncol. 2024 Jan;166(1):129-142. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04531-z. Epub 2024 Jan 15. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 38224404 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to modulate MGMT activity.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Sep 1;26(25):4189-99. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.5964. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18757334 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrins and p53 pathways in glioblastoma resistance to temozolomide.Front Oncol. 2012 Oct 31;2:157. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00157. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23120745 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis disturbs the characteristics of glioblastoma stem-like cells of rat RG2 glioblastoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Aug 21;13(1):85. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-85. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23961808 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis: Association between MGMT hypermethylation and the clinicopathological characteristics of non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 23;8(1):1439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19949-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29362385 Free PMC article.
-
Culture on 3D Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Scaffolds Enhances Stem Cell Marker Expression and Drug Resistance in Human Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016 Dec;5(24):3173-3181. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600684. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016. PMID: 27805789 Free PMC article.
-
MGMT DNA repair gene promoter/enhancer haplotypes alter transcription factor binding and gene expression.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016 Oct;39(5):435-447. doi: 10.1007/s13402-016-0286-4. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 27306526
References
-
- Samson L L, Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977;267:281–3. - PubMed
-
- Weller M, Stupp R, Reifenberger G, Brandes AA, van den Bent MJ, Wick W, Hegi ME. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: ready for personalized medicine? Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:39–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

