Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: distribution and functions
- PMID: 22245784
- PMCID: PMC3288509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.01.004
Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: distribution and functions
Abstract
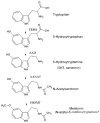
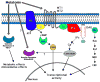
Many of melatonin's actions are mediated through interaction with the G-protein coupled membrane bound melatonin receptors type 1 and type 2 (MT1 and MT2, respectively) or, indirectly with nuclear orphan receptors from the RORα/RZR family. Melatonin also binds to the quinone reductase II enzyme, previously defined the MT3 receptor. Melatonin receptors are widely distributed in the body; herein we summarize their expression and actions in non-neural tissues. Several controversies still exist regarding, for example, whether melatonin binds the RORα/RZR family. Studies of the peripheral distribution of melatonin receptors are important since they are attractive targets for immunomodulation, regulation of endocrine, reproductive and cardiovascular functions, modulation of skin pigmentation, hair growth, cancerogenesis, and aging. Melatonin receptor agonists and antagonists have an exciting future since they could define multiple mechanisms by which melatonin modulates the complexity of such a wide variety of physiological and pathological processes.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abe K, Robison GA, Liddle GW, Butcher RW, Nicholson WE, Baird CE. Role of cyclic AMP in mediating the effects of MSH, norepinephrine, and melatonin on frog skin color. Endocrinology. 1969;85:674–682. - PubMed
-
- Anisimov VN. The role of pineal gland in breast cancer development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;46:221–234. - PubMed
-
- Anisimov VN, Ukraintseva SV, Yashin AI. Cancer in rodents: does it tell us about cancer in humans? Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:807–819. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama H, Mori W, Mori N. Anti-glucocorticoid effects of melatonin in young rats. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1986;36:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Arendt J. Melatonin. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1988;29:205–229. - PubMed

