Effect of cigarette smoke exposure and structural modifications on the α-1 Antitrypsin interaction with caspases
- PMID: 22245800
- PMCID: PMC3356416
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00207
Effect of cigarette smoke exposure and structural modifications on the α-1 Antitrypsin interaction with caspases
Abstract
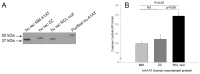
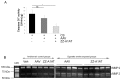
α-1 Antitrypsin (A1AT) is a serpin with a major protective effect against cigarette smoke-induced emphysema development, and patients with mutations of the A1AT gene display a markedly increased risk for developing emphysema. We reported that A1AT protects lung endothelial cells from apoptosis and inhibits caspase-3 activity. It is not clear if cigarette smoking or A1AT mutations alter the caspase-3 inhibitory activity of A1AT and if this serpin alters the function of other caspases. We tested the hypothesis that the caspase-3 inhibitory activity of A1AT is impaired by cigarette smoking and that the A1AT RCL, the key antiprotease domain of the serpin, is required for its interaction with the caspase. We examined the caspase-3 inhibitory activity of human A1AT purified from plasma of actively smoking and nonsmoking individuals, either affected or unaffected with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. We also tested the caspase inhibitory activity of two mutant forms of A1AT, the recombinant human piZZ and the RCL-deleted (RCL-null) A1AT forms. A1AT purified from the blood of active smokers exhibited marked attenuation in its caspase-3 inhibitory activity, independent of disease status. In vitro exposure of the normal (MM) form of A1AT to cigarette smoke extract reduced its ability to interact with caspase-3, measured by isothermal titration calorimetry, as did the deletion of the RCL, but not the ZZ point mutation. In cell-free assays A1AT was capable of inhibiting all executioner caspases, -3, -7 and especially -6, but not the initiator or inflammatory caspases. The inhibitory effect of A1AT against caspase-6 was tested in vivo, where overexpression of both human MM and ZZ-A1AT via adeno-associated virus transduction significantly protected against apoptosis and against airspace damage induced by intratracheal instillation of caspase-6 in mice. These data indicate a specific inhibitory effect of A1AT on executioner caspases, which is profoundly attenuated by active exposure to cigarette smoking and is dependent on the protein RCL, but is not affected by the PiZZ mutation.
Figures
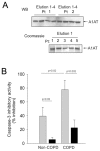
 , n = 13) or actively smoking cigarettes (■, n = 16).
, n = 13) or actively smoking cigarettes (■, n = 16).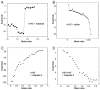
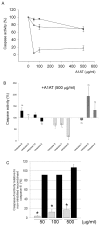
 ) were incubated with purified human A1AT (0–500 μg/mL). (B) Initiator caspases (recombinant active caspases -8, -9, -10, -2), executioner caspases (-3, -7, -6) or inflammatory caspases (-1, -4, -5) were incubated with purified human A1AT obtained from pooled plasma (500 μg/mL; n = 3). (C) Executioner caspase-6 incubated with purified A1AT (
) were incubated with purified human A1AT (0–500 μg/mL). (B) Initiator caspases (recombinant active caspases -8, -9, -10, -2), executioner caspases (-3, -7, -6) or inflammatory caspases (-1, -4, -5) were incubated with purified human A1AT obtained from pooled plasma (500 μg/mL; n = 3). (C) Executioner caspase-6 incubated with purified A1AT (
 ) or recombinant RCL-null A1AT (■) (0–500 μg/mL; n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus caspase-6 activity incubated with vehicle and versus RCL-null A1AT).
) or recombinant RCL-null A1AT (■) (0–500 μg/mL; n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus caspase-6 activity incubated with vehicle and versus RCL-null A1AT).
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Xu J, Murphy SL, Minino AM, Kung HC. Deaths: preliminary data for 2009. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2011;59:1–51. - PubMed
-
- Yokohori N, Aoshiba K, Nagai A. Increased levels of cell death and proliferation in alveolar wall cells in patients with pulmonary emphysema. Chest. 2004;125:626–32. - PubMed
-
- Poller W, Willnow TE, Hilpert J, Herz J. Differential recognition of -antitrypsin-elastase and -antichymotrypsin-cathepsin G complexes by the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2841–5. - PubMed
-
- Owen MC, Carrell RW. alpha-1-Antitrypsin: sequence of the Z variant tryptic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1977;79:245–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

