Electrophoretically induced aqueous flow through single-walled carbon nanotube membranes
- PMID: 22245860
- PMCID: PMC4134328
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2011.240
Electrophoretically induced aqueous flow through single-walled carbon nanotube membranes
Abstract
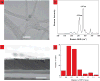
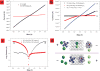
Electrophoresis, the motion of charged species through liquids and pores under the influence of an external electric field, has been the principle source of chemical pumping for numerous micro- and nanofluidic device platforms. Recent measurements of ion currents through single or few carbon nanotube channels have yielded values of ion mobility that range from close to the bulk mobility to values that are two to seven orders of magnitude higher than the bulk mobility. However, these experiments cannot directly measure ion flux. Experiments on membranes that contain a large number of nanotube pores allow the ion current and ion flux to be measured independently. Here, we report that the mobilities of ions within such membranes are approximately three times higher than the bulk mobility. Moreover, the induced electro-osmotic velocities are four orders of magnitude faster than those measured in conventional porous materials. We also show that a nanotube membrane can function as a rectifying diode due to ionic steric effects within the nanotubes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ion exclusion by sub-2-nm carbon nanotube pores.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 11;105(45):17250-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710437105. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18539773 Free PMC article.
-
DNA translocating through a carbon nanotube can increase ionic current.Nanotechnology. 2012 Nov 16;23(45):455107. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/45/455107. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Nanotechnology. 2012. PMID: 23090315 Free PMC article.
-
Gated ion transport through dense carbon nanotube membranes.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Jun 23;132(24):8285-90. doi: 10.1021/ja9091769. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20504021
-
Towards mimicking natural protein channels with aligned carbon nanotube membranes for active drug delivery.Life Sci. 2010 Apr 10;86(15-16):563-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 Apr 18. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 19383500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanochannels: biological channel analogues.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2012 Jun;6(2):63-70. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2011.0033. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22559709 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoporous Membranes of Densely Packed Carbon Nanotubes Formed by Lipid-Mediated Self-Assembly.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Feb 19;7(2):528-534. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00585. Epub 2022 Sep 7. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 36070609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A computational assessment of the permeability and salt rejection of carbon nanotube membranes and their application to water desalination.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016 Feb 13;374(2060):20150020. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0020. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016. PMID: 26712639 Free PMC article.
-
An Electrically Actuated, Carbon-Nanotube-Based Biomimetic Ion Pump.Nano Lett. 2020 Feb 12;20(2):1148-1153. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04552. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 31877247 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Electrochemical Membranes for Continuous Affinity Protein Separation.Adv Funct Mater. 2014 Jul 16;24(27):4317-4323. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201303707. Adv Funct Mater. 2014. PMID: 25383076 Free PMC article.
-
Mass transport through vertically aligned large diameter MWCNTs embedded in parylene.Nanotechnology. 2012 Nov 16;23(45):455101. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/45/455101. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Nanotechnology. 2012. PMID: 23064678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daugherty NA. Isoenzymes. J Chem Educ. 1979;56:442–447.
-
- Sarazin C, Delaunay N, Costanza C, Eudes V, Gareil P. Capillary electrophoresis analysis of inorganic cations in post-blast residue extracts applying a guanidinium-based electrolyte and bilayer-coated capillaries. Electrophoresis. 2011;32:1282–1291. - PubMed
-
- Kishi T, Nakamura J, Arai H. Application of capillary electrophoresis for the determination of inorganic ions in trace explosives and explosive residues. Electrophoresis. 1998;19:3–5. - PubMed
-
- Ferslew KE, Hagardorn AN, Harrison MT, McCormick WF. Capillary ion analysis of potassium concentrations in human vitreous humor. Electrophoresis. 1998;19:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Mrestani Y, Neubert R, Schiewe J, Härtl A. Application of capillary zone electrophoresis in cephalosporin analysis. J Chromat B: Biomed Sci Appl. 1997;690:321–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

